Multi Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud Understanding the Key Differences
0 likes | 43 Vues
The difference between hybrid cloud and multi-cloud is often unclear because people use these terms interchangeably. However, there is one significant difference. In a multi-cloud setup, a company uses various public cloud services, usually from different providers. While both have their merits, they serve different purposes and come with distinct advantages and challenges.<br><br>In this article, we will discuss the key differences between multi-cloud architecture and hybrid cloud to help you make informed decisions for your organizationu2019s cloud journey.

Multi Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud Understanding the Key Differences
E N D
Presentation Transcript
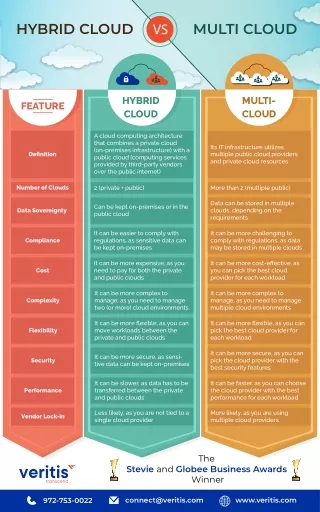
Multi Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud: Understanding the Key Differences The difference between hybrid cloud and multi-cloud is often unclear because people use these terms interchangeably. However, there is one significant difference. In a multi-cloud setup, a company uses various public cloud services, usually from different providers. While both have their merits, they serve different purposes and come with distinct advantages and challenges. In this article, we will discuss the key differences between multi-cloud architecture and hybrid cloud to help you make informed decisions for your organization’s cloud journey. UNDERSTANDING MULTI-CLOUD ARCHITECTURE Multi-cloud architecture, as the name suggests, involves the use of multiple cloud service providers to meet various business needs. This strategy aims to avoid vendor lock-in, enhance redundancy, improve disaster recovery capabilities, and optimize costs. Here are the primary characteristics of multi-cloud architecture:
1. Vendor Diversity In a multi-cloud setup, organizations use the services of two or more cloud providers simultaneously. This diversity in vendors offers flexibility and prevents dependency on a single provider, mitigating risks associated with service outages or pricing fluctuations. 2. Best-of-Both Approach Multi-cloud architecture allows organizations to select the best-in-class services from different providers. For instance, an organization might use AWS for its robust machine learning capabilities, Google Cloud for data analytics, and Azure for its enterprise-grade infrastructure. 3. Geographic Distribution To improve data redundancy and disaster recovery, organizations can deploy resources across multiple geographic regions offered by different cloud providers. This ensures that data and applications remain accessible even in the event of regional outages. 4. Cost Optimization Multi-cloud can offer cost advantages by strategically utilizing providers’ pricing models, optimizing resources, and avoiding overcommitting to a single provider’s offerings.
5. Complexity Managing resources across multiple cloud providers can introduce complexity in terms of monitoring, security, and governance. It requires a robust cloud management strategy and the right set of tools. UNDERSTANDING HYBRID CLOUD Hybrid cloud, on the other hand, combines on-premises infrastructure with cloud resources, providing a seamless and integrated environment. This approach is ideal for organizations looking to maintain control over sensitive data and applications while benefiting from the scalability and flexibility of the cloud. Here are the primary characteristics of hybrid cloud benfits : 1. Integration of On-Premises and Cloud In a hybrid cloud setup, organizations maintain some infrastructure on-premises while leveraging cloud resources for specific workloads. This integration ensures smooth data and application flow between the two environments. 2. Data Privacy and Compliance Hybrid cloud caters to organizations with strict data privacy and compliance requirements. Critical or sensitive workloads can be kept on-premises, while less sensitive workloads can run in the cloud.
3. Scalability and Bursting Organizations can scale their operations dynamically by utilizing cloud resources during peak periods and relying on on-premises infrastructure during normal workloads. This flexibility optimizes costs and ensures resource availability. 4. Complex Workloads Hybrid cloud is suitable for complex workloads that require a combination of on- premises and cloud resources. For example, an organization might keep its legacy applications on-premises while using cloud-based AI and machine learning services. 5. Network Connectivity A robust and high-speed network connection is crucial for hybrid cloud setups to ensure efficient communication between on-premises and cloud environments. KEY DIFFERENCES BETWEEN MULTI-CLOUD AND HYBRID CLOUD Now that we have a clear understanding of both multi-cloud architecture and hybrid cloud, let’s explore the key differences between the two approaches: 1. Infrastructure Ownership Multi-Cloud: Organizations do not own the underlying infrastructure. Instead, they subscribe to cloud services from different providers.
Hybrid Cloud: Organizations retain ownership of on-premises infrastructure, which is integrated with cloud resources. 2. Data and Workload Placement Multi-Cloud: Data and workloads can be distributed across multiple cloud providers’ data centers. Hybrid Cloud: Data and workloads are strategically placed either on-premises or in the cloud, depending on requirements. 3. Use Cases Multi-Cloud: Ideal for organizations seeking flexibility, vendor diversity, and best-of-breed services across multiple cloud providers. Hybrid Cloud: Suited for organizations with a mix of legacy systems, sensitive data, and scalability needs. 4. Complexity Multi-Cloud: May introduce complexity in terms of managing resources across different providers. Hybrid Cloud: Requires robust integration and networking but may be simpler to manage compared to multi-cloud.
5. Data Privacy and Compliance Multi-Cloud: Offers options for compliance but may require careful management of data sovereignty. Hybrid Cloud: Ideal for organizations with strict data privacy and compliance requirements, as sensitive data can be kept on-premises. 6. Network Connectivity Multi-Cloud: Requires robust network connectivity between the organization’s network and multiple cloud providers. Hybrid Cloud: Demands a high-speed and reliable network connection to ensure seamless communication between on-premises and cloud environments. CHOOSING THE RIGHT CLOUD STRATEGY Selecting the right cloud strategy depends on your organization’s unique needs and objectives. Here are some considerations to help you make an informed decision: Workload Assessment: Evaluate your workloads and determine which are best suited for the cloud, on-premises, or a combination of both. Data Sensitivity: Consider the sensitivity of your data and compliance requirements. If you deal with highly sensitive data, a hybrid approach might be more suitable.
Scalability Requirements: Assess your scalability needs. If your organization experiences fluctuating workloads, a hybrid or multi-cloud approach can provide flexibility. Complexity Tolerance: Determine your organization’s tolerance for managing complex cloud environments. If simplicity is a priority, a hybrid cloud might be more manageable. Resource Ownership: Consider whether you want to maintain ownership of on-premises infrastructure or prefer to rely entirely on cloud providers. Cost Optimization: Evaluate the cost implications of each approach. Multi- cloud can provide cost advantages if managed effectively, while a hybrid cloud might help control costs for specific workloads. CAN A HYBRID CLOUD ALSO BE MULTI-CLOUD? Yes, a hybrid cloud can become multi-cloud when it combines more than one public cloud service with private cloud resources. A hybrid cloud is a mix of public and private clouds used to manage a single IT solution. It is often built on a common virtualization layer like VMware cloud or vSphere. By including VMware on AWS course and VMware on-premises, a hybrid cloud simplifies workload migration and enables the use of common tools across both private and public cloud platforms. On the other hand, multi-cloud involves using multiple cloud services from one or more providers, such as AWS for application workloads and Microsoft Azure for enterprise databases. Unlike a hybrid cloud, multi-cloud specifically refers to
more than one public cloud provider service and may not include a private cloud component at all. Enterprises adopt a multi-cloud strategy to avoid relying on a single provider, comply with geographic or regulatory governance demands, ensure business continuity, or take advantage of features specific to a particular provider. In conclusion, both multi-cloud architecture and hybrid cloud have their merits and are valuable strategies in different contexts. Organizations must carefully assess their requirements, data sensitivity, and scalability needs to make the right choice. It’s also crucial to have a well-defined cloud management and governance strategy to ensure the successful implementation of either approach. To gain a deeper understanding and hands-on experience with multi-cloud architecture, consider enrolling in Datavalley’sMulti Cloud Solutions Architect Master’s Program. This comprehensive training program will equip you with the knowledge and skills needed to design, deploy, and manage multi- cloud environments effectively. Make an informed decision, embrace the cloud strategy that aligns with your organization’s goals, and embark on a successful cloud journey. BECOME A CLOUD ARCHITECT WITH DATAVALLEY Attaining superior training is crucial for achieving success in the realm of cloud computing and staying ahead of evolving trends and technologies. Datavalley’sMulti Cloud Solutions Architect Master’s Program is a comprehensive initiative that will furnish you with the expertise and understanding required to flourish in the cloud sector.
Course Highlights: •Gain knowledge from specialists in the field who have practical experience in cloud architecture and emerging technologies. •Stay up-to-date with the latest cloud trends, including edge computing, serverless computing, Google Professional Cloud Architect, AWS Solutions Architect Professional, Azure Administrator Associate, DevOps Foundation Course. •Gain practical experience through hands-on labs, real-world projects, and live classes. •Up to 70% scholarship on all our courses. •Obtain a reputable certification that confirms your skills as a cloud architect master program. •Connect with other professionals who share your interests and build relationships with experts in your field. •There are various learning formats to choose from, including online courses and self-paced modules. •Our experts will provide you with up to 3 months of on-call project assistance to help you succeed in your new role. Take the first step and unlock endless possibilities in the ever-evolving cloud landscape. Enroll in Datavalley’sMulti Cloud Solutions Architect Master’s Program to prepare for the future of cloud computing training.