BLOOD
120 likes | 313 Vues
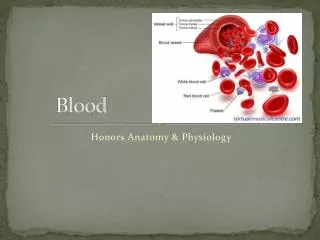
BLOOD. WHAT IS IT?. BLOOD. Consists of two distinct elements: Plasma : fluid portion (55%) Water Dissolved gases: _____________________ Proteins Sugars Vitamins Minerals waste Formed : composed of cells (45%) Mostly red and white blood cells. Red Blood Cells.

BLOOD
E N D
Presentation Transcript
BLOOD WHAT IS IT?
BLOOD • Consists of two distinct elements: • Plasma: fluid portion (55%) • Water • Dissolved gases: _____________________ • Proteins • Sugars • Vitamins • Minerals • waste • Formed: composed of cells (45%) • Mostly red and white blood cells.
Red Blood Cells • Also called ERYTHROCYTES • Make of 44% of the 45% “formed” part of blood. • Specialized for ____________ transport. • Mature cell has no nucleus • Packed with respiratory pigment called HEMOGLOBIN: iron-containing molecule that binds with oxygen.
Blood Colour is Determined by Different Respiratory Pigments • You may have noticed the different colours of fluid produced by ‘squished’ organisms... this is partially the reason:
White Blood Cells • Also called LEUCOCYTES. • Make up only about 1% of blood volume. • Play a major role in helping body fight off pathogens. • HAVE NUCLEI!
Platelets • Not cells. • Fragments of cells from bone marrow. • Important role in clotting blood protection from excessive blood loss after injury. • Steps to blood clotting (still not completely understood): • Blood vessel broken substances released by broken blood vessels attract platelets platelets rupture and chemicals released thromboplastin (enzyme) is produced reacts with prothrombin to produce thrombin reacts with fibrinogen fibrin. • Fibrin: insoluble material that forms a mesh of strands around an area of injury. • Traps escaping blood cells!
Blood Plasma • Medium in which blood cells/platelets are suspended • Contains dissolved proteins which are important to all blood functions: • Red blood cell processes • White blood cell processes • Platelet processes, • Etc.
Classwork/Homework • Read “Human Blood Groups” (page 300) and make detailed notes. • Complete the following SR questions (page 303) • #1, 2, 4, 8, 9, 11.