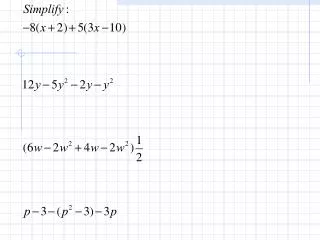Mastering GIS: Beyond Basics
450 likes | 563 Vues
Elevate your GIS skills with advanced topics including vector and raster GIS, spatial modeling, remote sensing, and database management. Dive into ArcGIS for editing, analysis, and data models. Small class, rich learning experience.

Mastering GIS: Beyond Basics
E N D
Presentation Transcript
But First ... An AD from your Friendly Nieghborhood GIS Instructor
What’s Next • To be really accomplished in GIS (or GIT) you need the following … • Vector GIS (You got it) • Raster GIS (FOR556) • Expert in Vector GIS (FOR558) • GPS FEG XXX • Remote Sensing FEG XXXXXXX • Database management (FEG xxxx)
For Science & Engineering • Biology – Raster and Vector …For556 and Myra Hall’s xxxx (final project can be same for both) • Landscape Architecture – Vector GIS (FOR558) and AutoCad • Forestry – Vector GIS (FOR558 & 556) • Engineering (see previous slide)
For556, Spatial Modeling • Use IDRISI to solve problems dependent on continuous surfaces ( elevation, water table, viewsheds, etc.) • Emphasis is NOT on learning the software – that is easy • Emphasis is on Creative Thinking through applying the technology to problem solving • Like 557 has weekly exercises that provide less cookbook instructions as the semester progresses • Quizzes but no exams; final problem
FOR558 Advanced Topics The latest and greatest development in GIS • Next semester will be ArcGIS • Emphasis on • Editing vector data – a tricky business in ArcGIS • Analysis • Using Data Models like • ArcHydro for hydrologic modeling • Forestry Data Model for forest management • Planning Data Model • Grid processing and modeling
FOR558 Advanced Topics • Next semester will be ArcGIS • Emphasis on • Editing vector data – a tricky business in ArcGIS • Analysis • Using Data Models like • ArcHydro for hydrologic modeling • Forestry Data Model for forest management • Planning Data Model • Grid processing and modeling Small class – exact topics covered depends of interests of enrollees
Sales Pitch Over On to Analysis In 9
Analysis • Starts with selection… • Why? • Because • Many steps in analysis are simply selection by • Attribute • Location • Most of the OVERLAY functions’ operations depend on what features are selected
Here are some actions… • Check that • Layer(s) are the ones you want • The selection options are what you want • Check the bottom of the dialog and make sure it is doing what you want it to • That sounds easy but quite often NOT easy • Here are some of the options
Allow the selection of features that certain criteria Is a pretty rich set of operations BUT Some share name with the REAL overlay operations but don’t deliver the same result Intersect Within distance of Completely contain Completely within Have center in Share segment w/ Touch boundary of Are identical to Are crossed by outline Contain Are contained by Selection Summary
Overlay Operations • Overlay operations are like the “select by location” functions but not exactly the the same. • Both use two layers • Select by location just selects features • Overlay operations create new feature classes
Overlay: Erase • From Help: Erase feature removes a chunk of the input feature • It is important to keep Input and Erase feature correct or GIGO
Overlay: Union • This computes a geometric intersection of the input and output feature classes . ALL features will be written to the output feature class with the attributes from both. • Or: This tool builds a new feature class by combining the features and attributes of each feature class.
Overlay: Union • The geometric Intersection of the input and output feature classes • ALL features will be written to the output feature class with the attributes from both. • Or: This tool builds a new feature class by combining the features and attributes of each feature class.
Overlay: Identity • Computes a geometric intersection (logic) of the input and identity features • Input features (or portions thereof) that overlap the identity features will get their attribute features from the identity features • To put it another way: combines the portions of features that overlap the identity features to create a new feature class.
Overlay: Identity • Computes a geometric intersection (logic) of the input and identity features • Input features (or portions thereof) that overlap the identity features will get attribute features from the identity features • To put it another way: combines the portions of features that overlap the identity features to create a new feature class. Clips by the Input feature and then UNIONS what is left.
Overlay: Intersect • Computes the geometric intersection of the input features or portions of features COMMON to all layers. • This tool builds a new feature class from the intersecting features common in both feature classes. Available with any ArcGIS license.
Intersect is NOTthe same asIdentity Overlay: Intersect • Computes the geometric intersection of the input features or portions of features COMMON to all layers. • This tool builds a new feature class from the intersecting features common in both feature classes. Available with any ArcGIS license.
Overlay: Symmetric Diff • Computes a geometric intersection of the input and update features. Any features COMMON to ONLY one of the inputs will be written to the output • Or to put it another way: This tool creates a feature class from those features or portions of features that are not common to any of the other inputs.
Overlay: Symmetric Diff This is the olive drab feature showing through a hole in the yellow feature! • Computes a geometric intersection of the input and update features. Any features COMMON to ONLY one of the inputs will be written to the output • Or to put it another way: This tool creates a feature class from those features or portions of features that are not common to any of the other inputs.
Overlay: Update • Computes the geometric intersection of the input and update features. The attributes and geometry of the input features are replaced by the update features. • This tool updates the attributes and geometry of an input feature class or layer by the Update feature class or layer that they overlap
Overlay: Update • Computes the geometric intersection of the input and update features. The attributes and geometry of the input features are replaced by the update features. • This tool updates the attributes and geometry of an input feature class or layer by the Update feature class or layer that they overlap
Overlay: Summary IDENTITY INTERSECT SYM-DIF UNION UPDATE
Buffer • Buffering is an additional tool used in Analysis.
Summary • The analysis tool in ArcGIS are very powerful • And fairly easy to understand … one at a time! • It is use by combining the overlay and selection tools to solve a problem that is the problem!
A Problem • Find location for a laboratory • Within 300 meters of a sewer line • NOT within 200 meters of a stream • Parcel in a specific landuse (900 is forest) • Not on steep slopes (<=20%) • >=100 acres but less than 200 acres • THIS IS A CLASSIC LOCATION PROBLEM
Buffer Sewbuf 300 Sewer OK ERASE Buffer Strmbuf 20 OK sites IDENTITY Query IDENTITY Of selectedpolys Land OK Query Sewers w/in 300m Streams not w/in 20m Landuse: Lucode =? Slope<=20%
Booby Trap • Select by location using Intersect does not give the same results as Overlay Intersect
Sel by Theme: Intersection • Intersected Parcels w/ Cover with Ag Selected • The red outlines are the selected parcels Lets Zoom In ----
You can see that Entire Parcels were selected Parcels with only a little bit of Ag landuse were selected Select by theme
BUT THE RESULT IS VERY DIFFERENT! Overlay Intersection Red outlines are the parcels selected by Select by theme Green are the result of the Overlay
So you have to be careful! • Exercise 6 has you experiment with some simple layers • And I will be throwing some relatively simple problems your way to provide more practice • And I will be changing the schedule at bit too (what else is new?).