E-Business Strategy Models: The Amazon Story
240 likes | 423 Vues
Explore Amazon's e-business models, including online retailing, co-branding partnerships, and affiliate programs. Learn strategic objectives and models for e-business success.

E-Business Strategy Models: The Amazon Story
E N D
Presentation Transcript
[C]E-Business Strategy/ Models • 參考資料: • Judy Strauss, Adel I. El-Ansary, and Raymond Frost, E-Marketing, Prentice Hall, 2006. • Chap 2: Strategic E-Marketing. • Chap 12: Distribution. • Ward Hanson, Principles of Internet Marketing.
Environment, Strategy, and Performance (ESP Model) Legal - Ethical Technology Internet E Competition Other factors Markets SWOT E - Business S Strategy/ E - Marketing Implementation Marketing Mix Model Strategy P Performance Metrics
Overview • The Amazon Story • E-Business Strategy • E-Business Model • Strategic E-Business Models • Activity Level E-Business Models • Business Process Level E-Business Models • Enterprise Level E-Business Models • Pure Play • Web Business Models
1. The Amazon Story • Amazon (http://www.amazon.com) • Jeff Bezos於1995年7月創辦 • A pure-play dot-com (純網路公司) survivor. • Adapt its competencies into many different e-business models. • 成功秘訣:善用IT,為其顧客及聯盟夥伴間建立關係及品牌忠誠度 • 與顧客建立一對一關係,進行顧客化推薦 • 與內容網站建立聯盟關係,快速建立銷售據點
E-Business Model of Amazon • (1) Online Retailing • Amazon’s core business: Sales of books, music, and videos. • After 7 years of effort, Amazon.com finally proved this model can be profitable. • Learn a good, but tough (痛苦) , formula for operating profitability. • 2002-2003, Amazon has cut inventory by 25%, tightened (拴緊) operations, and doubled sales.
E-Business Model of Amazon • (2) Co-branding (聯合品牌) Partnership • Include Borders, Circuit City, Target, and Toys “R”Us (玩具反斗城). • These partnerships involve Amazon’s licensing of online storefront technology or earning fees for customer service and product delivery. • This model is more profitable than retailing model. • Because its less costly automated services, e-commerce experience, or huge customer base. • Amazon’s objective: add 2 new partners /1 year.
E-Business Model of Amazon • (3) Affiliate Program (結盟方案) • Amazon create firstly. (called Amazon Associates) • Giving 600,000 Web site owners a 15% commission (銷售佣金) for referring (指引) customers who purchase at Amazon. • (4) Auction (拍賣) • Customers can auction items on the site.
2. E-Business Strategy • Corporate Strategy • It is concerned with how the firm will achieve its objectives. • Strategic planning = the “managerial process of developing and maintaining a viable (可行的) fit between the organization’s objectives, skills, resources and its changing market opportunities.” • E-Business Strategy = Corporate Strategy + Information Technology
Strategic Objectives • The firm sets objectives such as: • Growth. How much can the firm reasonably expect to grow in terms of revenues, and how fast? • Competitive position. How should the firm position itself against other firms in the industry? Viable positions are: • Industry leader (Microsoft), • Price leader (Priceline.com), • Quality leader (Mercedes), • Niche firm (Google.com), • Best customer service (Dell.com).
Strategic Objectives (Cont.) • Geographic scope. Where should the firm serve its customers on the continuum (連續光譜) of local to multinational? • Other objectives. Companies often set objectives for the number of industries they will enter, the range of products they will offer, the core competencies they will foster (培養), and so on.
3. E-Business Model • Business Model • A method by which the organization sustains (支持) itself in the long term, and includes its value proposition (價值提案) for partners and customers as well as its revenue streams (收入來源). • A firm will select one or more business models as strategies to accomplish enterprise goals. • E-Business Model = Business Model + Information Technology
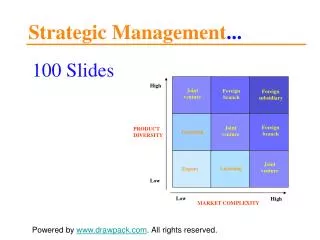
Pure Pure dot - com Business transformation (Amazon) Play (competitive advantage, industry redefinition) Level of business impact Enterprise most retailers Effectiveness Customer (customer Business Process Relationship retention) Management Efficiency Activity (cost E-mail reduction) 4. Strategic E-Business Models • Level of Commitment to E-business
E-Business Model Classification • The lowest level of the pyramid • Affects individual business activities that can save the firm money if automated using IT or Internet.
E-Business Model Classification • The second level of the pyramid • Changes business processes to increase the firm’s effectiveness.
E-Business Model Classification • The enterprise level of the pyramid • The firm automates many business processes in a unified system- demonstrating a significant commitment to e-business.
Agent Models Representing Sellers (賣方代理人) • Selling Agents. Represent a firm to help sell products. • Manufacturer’s Agents. Represent manufacturing firms. • Catalog Aggregator. Brings together many catalog companies to create a new searchable database of products for buyers. • Metamediary. Represents a cluster of manufacturers, online retailers, and content providers organized around a life event (如結婚) or major asset purchase (如購屋).
Agent Models Representing Buyers (買方代理人) • Shopping Agents. Help individual consumers find specific products and the best prices online. • Reverse Auction. Allows individual buyers to enter the price they will pay for particular items at the purchasing agent’s Web site, and sellers can agree or not. • Buyer Cooperative (買方代表, or Buyer Aggregator). Pools many buyers together to drive down the price on selected items. (代表多個買方進行集體議價)
Virtual Mall • is similar to a shopping mall in which multiple online merchants are hosted at a Web site. • Infomediary (資訊中間商) • is an online organization that aggregates and distributes information. • E.g.: market research firms.
E-Business Model Classification • Businesses that began on the Internet, even if they subsequently added a brick-and-mortar (實體) presence. • Pure plays face significant challenges. • They must compete as new brands and take customers away from established brick-and-mortar businesses. • One way to change the rules is to invent a new e-business model, as Yahoo! and eBay did.
5. Web Business Models • 以網路對公司所帶來的效益來區分 • Business models can be based on improvements in product or service • 以產品或服務改進為基礎的經營模式 • Business models can be based directly on generating revenue • 以直接收入為基礎的經營模式
Build brand Build category Enhance quality 5.1 Improvement-Based Business Models (1) Enhancement (2) Efficiency • Reduce costs • Free trial (3) Effectiveness • Support dealers • Support suppliers
5.2 Revenue-Based Business Models (1) Provider Pays (2) Customer Pays 由想要接觸網站用戶的公司 向網站支付費用的模型 包含B2B及B2C的交易收入 • Product sales • Pay-per-use • Subscriptions(預約訂閱或會費) • Bundle sales (包裹銷售) • 例如美國科學雜誌線上版僅提供給印刷本的訂閱者 • Sponsorship (內容贊助) • Alliances (零售聯盟) • Banner advertising • Prospect fees (服務費或點選接通費) • Sales commissions