Task Transition Management System: An Analysis on Performance Verification
80 likes | 165 Vues
Dive into the analysis of task scheduling, anomalies, and control systems in this paper summary session by Alessadro Pinto. Learn about reachability, soundness, and fair treatment guarantees in managing work items efficiently. Discover the implications of workflow execution based on state charts and activity charts in distributed environments. Explore tools, models, and concerns related to workflow performance and verification.

Task Transition Management System: An Analysis on Performance Verification
E N D
Presentation Transcript
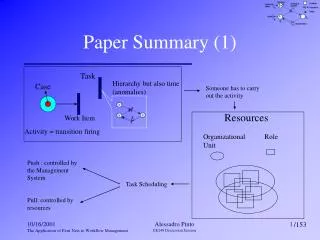
Task Hierarchy but also time (anomalies) Case Someone has to carry out the activity Resources Work Item Activity = transition firing Organizational Unit Role Push : controlled by the Management System Task Scheduling Pull: controlled by resources Paper Summary (1) Alessadro Pinto EE249 Discussion Session /153
Validation • P, T invariants • Reachability • Coverability It’s time to analyze Analysis Verification Performance • Throughput • Resource occupation • Soundness (dynamic) • For every state M reachable from state I, there exists a firing rule sequence leading from state M to state o • State o is the only state reachable from state i with at least one token is place o • There are no dead transition (A case must be finished!) The analysis will abstract from trigger, color (non deterministic). Abstraction is needed. Paper Summary (2) Alessadro Pinto EE249 Discussion Session
Paper Summary (3) I forgot fairness in the previous slide. Very important because: Soundness and Fairness Guarantee that each case will end in place o eventually A WF PN is sound if and only if is Live and Bounded PN o i We know how to handle it Alessadro Pinto EE249 Discussion Session
Paper Summary (4) Sound Safe S-Coverable PN Sound WS FC (iff starting from each place it is possible to identify a subnet that is strongly connected, is a state machine and for each place in the subnet, each transition connected to that place belong to the subnet) Sound FC WS S-C • Always safe • S-cov. Cheched in pol. time • Soundess is NP-complete WS FC • A FC PN can be checked for soundness in polynomial time • NFC PNs may have anomalous behaviors difficult to trace Well-Structured PN Free-choice PN (Balanced AND/OR-splits and AND/OR-joins) • Confusion • There are NFC PN that correspond to WF • There are FCPN that make no sense A WS PN can be checked for soundness in polynomial time Alessadro Pinto EE249 Discussion Session
Discussion (1) • Why PN? • What about FSMs? • D. Wodtke, G. Weikum, A Formal Foundation For Distributed Workflow Execution Based on State Charts,Proc. International Conference on Database Theory, 1997 • Muth, P., Wodtke, D., Weissenfels, J., Weikum, G., Kotz Dittrich, A., Enterprise-wide Workflow Management based on State and Activity Charts, in: A. Dogac, L. Kalinichenko, T. Ozsu, A. Sheth (Eds.): Workflow Management Systems and Interoperability, Springer Verlag, 1998 Alessadro Pinto EE249 Discussion Session
Discussion (1.1) • In fact only 4 tools that constitute 1 complete toolset are presented that are based on PN • Not enough to have a clear idea of what’s going on in the real world • The Author says that many tools are not based on PN. Which are the other model? Are they formal? Is it possible to verify the property? Alessadro Pinto EE249 Discussion Session
Discussion (2) • Othogonalization of concerns • Computation vs. Communication • Task vs. Resource • What about interoperability? • Communication between different WFP engine Alessadro Pinto EE249 Discussion Session
Little demo and links (I had to many things to do, it’s all I could do) ExSpect (Performance Analysis) exspect.com Protos (Design) pallas.nl Woflan (verification) http://tmitwww.tm.tue.nl/research/workflow/woflan/ http://www6.software.ibm.com/FlowMark/demo1.htm http://www.daimi.au.dk/PetriNets/ http://wwwis.win.tue.nl/~wsinwa/tools.html Alessadro Pinto EE249 Discussion Session