Classification Systems
170 likes | 430 Vues
Classification Systems. Why classify organisms? What are characteristics of a good classification system?. Why classify organisms?. Assigns a universally accepted name. Groups have biological meaning. Swedish Botanist Systema Naturae Binomial nomenclature Genus specific epithet example:

Classification Systems
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Classification Systems • Why classify organisms? • What are characteristics of a good classification system?
Why classify organisms? • Assigns a universally accepted name. • Groups have biological meaning.
Swedish Botanist Systema Naturae Binomial nomenclature Genus specific epithet example: Homo sapiens Carolos Linnaeus (1707-1778)
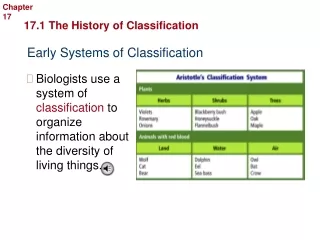
Systema Naturae • printed in the Netherlands in 1735. It was an eleven page work. • By the time it reached its 10th edition (1758), it classified 4,400 species of animals and 7,700 species of plants.
Taxonomy • “The science of naming organisms and assigning them to groups.” • Taxa- groups to which Linnaeus assigned organisms; taxon (singular) • The biological classification of organisms is based on a set of rules.
Taxa King- Kingdom Phillip- Phylum Came- Class Over- Order For- Family Green- Genus Spaghetti- Species
The Five Kingdoms • Monera- bacteria and blue-green algae (prokaryotes) • Protista- unicellular organisms (eukaryotes) • Fungi- yeasts, molds, mushrooms, heterotrophs • Plantae- vascular plants, photosynthetic • Animalia- metazoans, heterotrophs
Biological Species Concept • A species is a population of organisms that actively or potentially interbreed, producing viable offspring and which remain reproductively isolated from other such populations.
How many species are there on Earth? Current estimates of the total number of species on Earth range from 5 to 30 million (Environmental Literacy Council). The 2005 Millennium Ecosystem Assessment notes approximately 2 million have been formally described.
Over half of all described species are insects, including nearly 300,000 known beetles.
Recently Extinct Species Dodo Bird Thylacine- “Tasmanian Wolf”