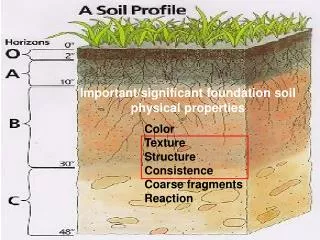
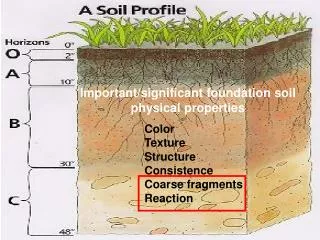
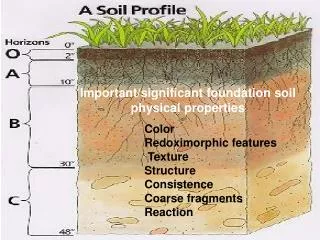
Soil Physical Properties
130 likes | 836 Vues
Soil Physical Properties. Soil Physical Properties. Color Texture Density (particle density vs. bulk density) Pore space (porosity) Structure Aggregate stability. Physical properties are important. 1) Control plant growth through influence on:. Soil temperature (darker = warmer).

Soil Physical Properties
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Soil Physical Properties • Color • Texture • Density (particle density vs. bulk density) • Pore space (porosity) • Structure • Aggregate stability
Physical properties are important 1) Control plant growth through influence on: Soil temperature (darker = warmer) Soil aeration (sandy soils well aerated) Soil moisture content (clayey soils stay wet) 2) Indicate important characteristics of a soil • e.g., lots vs. little organic matter
Objectives • Know what color tells you about a soil • Describe the concept of soil texture and its importance • Use the textural triangle to determine a soil’s textural class based on its sand, silt and clay content
Physical properties – Color • covaries with • O.M. • Fe and Al oxides • moisture saturation • mineralogy (e.g., calcite, hematite=Fe2O3) • Color
Color “quantified” using the Munsell system • Hue (e.g., 10YR) tells you general shade (red, yellow); DOES NOT tell you how dark the soil is • Value (e.g., 10YR 5/6) tells you how dark the soil is: 0 is darkest • Chroma (e.g., 10YR 5/6) tells you brightness (0 = gray). Indicates moisture conditions (bright = dry)
10R 10YR 10R 10P 10Y 10Y 10B 10G Soil Color: Hue 2.5 YR 5YR 7.5 YR 2.5 Y 5 Y 7.5 Y Go clockwise to numerically add next color!
10YR page of Munsell color book (also see Fig 4.1 of your text)
Example Question • Which soil horizon likely has more organic matter, one that is classified as 5R 5/6, or one that you decide is 10YR 1/7?