Two-View Geometry
220 likes | 416 Vues
Two-View Geometry. Jana Kosecka George Mason University. General Formulation. Two view geometry. Pinhole Camera Imaging Model. Image points. First frame is the reference. Second frame. Moving camera. Rigid Body Motion – Two Views.

Two-View Geometry
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Two-View Geometry Jana Kosecka George Mason University
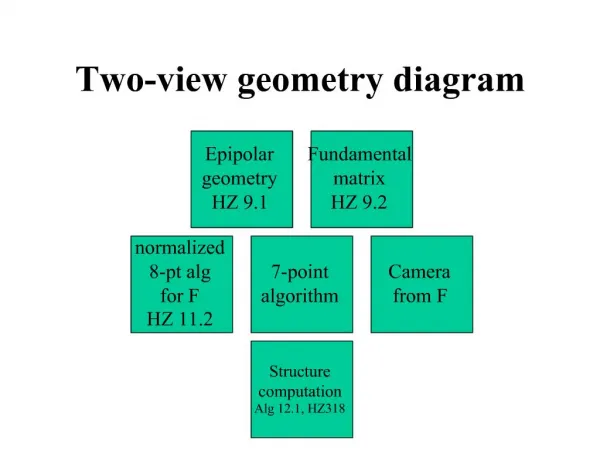
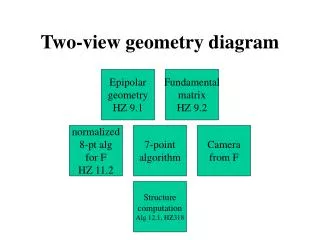
General Formulation Two view geometry ICRA 2003
Pinhole Camera Imaging Model • Image points First frame is the reference Second frame • Moving camera ICRA 2003
Rigid Body Motion – Two Views Camera motion is represented as the special Euclidean group ICRA 2003
3D Structure and Motion Recovery Euclidean transformation measurements unknowns Find such Rotation and Translation and Depth that the reprojection error is minimized Optimization ICRA 2003
Two views ~ 200 points 6 unknowns – Motion 3 Rotation 3 Translation - Structure 200x3 coordinates - (-) universal scale Difficult optimization problem ICRA 2003
Epipolar Geometry Image correspondences Algebraic Elimination of Depth [Longuet-Higgins ’81]: Essential matrix
Epipolar Geometry • Epipolar lines • Epipoles Image correspondences ICRA 2003
Characterization of Essential Matrix Essential matrix Special 3x3 matrix Theorem 1a(Essential Matrix Characterization)[Huang and Faugeras] A non-zero matrix is an essential matrix iff its SVD: satisfies: with and and ICRA 2003
Pose Recovery from Essential Matrix Essential matrix Theorem 1a (Pose Recovery) There are two relative poses with and corresponding to a non-zero matrix essential matrix. • Twisted pair ambiguity ICRA 2003
Estimating Essential Matrix Space of all Essential Matrices is 5 dimensional 3 Degrees of Freedom – Rotation 2 Degrees of Freedom – Translation (up to scale !) Special 3x3 matrix Essential matrix Given n pairs of image correspondences: Find such Rotation and Translation that the epipolar error is minimized ICRA 2003
Estimating Essential Matrix denote rewrite collect constraints from all points
Estimating Essential Matrix E • Solution • eigenvector associated with the smallest eigenvalue of • if degenerate configuration
Projection on to Essential Space E Theorem 2a (Project to Essential Manifold)[Toscani and Faugeras ’86] If the SVD of a matrix is given by then the essential matrix which minimizes the Frobenius distance is given by with
Two view linear algorithm (8-point) • Solve the LLSE problem: followed by projection • Projectonto the essential manifold: E is 5 diml. sub. mnfld. in SVD: • 8-point linear algorithm • Recover the unknown pose: ICRA 2003
Pose Recovery There are exactly two pairs corresponding to each essential matrix . There are also two pairs corresponding to each essential matrix . Positive depth constraint - used to disambiguate the physically impossible solutions • Translation has to be non-zero • Points have to be in general position • - degenerate configurations – planar points • - quadratic surface • Prerequisite – we need to have the correspondence of at least • 8 points • Nonlinear 5-point algorithms yield up to 10 solutions ICRA 2003
3D Structure Recovery • Eliminate one of the scale’s • Solve LLSE problem ICRA 2003
Summary • If the configuration is non-critical, the Euclidean structure of then points and motion of the camera can be reconstructed up to a universal scale. ICRA 2003
Rigid Body Motion – Continuous Case Image velocities Perspective Projection: • Image points First frame is the reference ICRA 2003
Two views differential case Algebraic elimination of depth Only symmetric component of can be recovered Differential epipolar constraint Continuous Essential Matrix ICRA 2003
Continuous Essential Matrix Special Symmetric Component Theorem 1b(Special Symmetric Matrix Characterization) A matrix is a special symmetric matrix iff it can be diagonalized as with and . Theorem 2b (Project to Special Symmetric Space) If a symmetric matrix is diagonalized as with and then the special symmetric matrix which minimizes the Frobenius distance is given by with ICRA 2003
Two view Linear Algorithm (continuous case) Sllse • Solve the LLSE problem: , S is 5 diml. sub. mnfld. in • Project onto the special sym. space: • Recover from