Priority Focus Process
180 likes | 328 Vues
Priority Focus Process. George Mason University College of Nursing and Health Science Regulatory Requirements for Health Systems Summer 2004. Used with Permission. Overview of the Priority Focus Process. PFP provides the process and infrastructure for the purpose of:

Priority Focus Process
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Priority Focus Process George Mason University College of Nursing and Health Science Regulatory Requirements for Health Systems Summer 2004 Used with Permission
Overview of the Priority Focus Process • PFP provides the process and infrastructure for the purpose of: • Converting pre-onsite survey data into information • Focusing on-site survey activities • Increasing consistency in the accreditation process • Customizing the accreditation process
Changing Data Into Information • PFP uses automation to gather pre-survey data from multiple sources • Joint Commission data (QMS, ORYX Core Measure) • Data supplied by the HCO (E-app,Periodic Performance Review ) • Publicly available data (MedPar) • PFP then applies “rules” to identify • Potential processes and clinical service groups to address • Relevant standards • Appropriate on-site survey activities
Future Rules Driven Priority Focus Process . . . Complement Standards APS Rules E-App Length Previous On-site Survey Data Fee QMS, ORYX Data PriorityFocus Rules PFP Output: Priority Issues, Relevant Standards, Survey Activity Medpar Data, Periodic Performance Review Data APS = Application Processing System
PFP Information • Includes the top 4-5 critical focus areas specific to the organization • Includes the clinical service groups most relevant to the organization • Organizations have access to their PFP information (on the Extranet) at the 15-month point with Periodic Performance Review and 1-2 weeks prior to survey
Priority Focus Process: Outputs – Critical Focus Areas • PFP displays an organization’s priority Critical Focus Areas (CFAs) • Critical Focus Areas are processes, systems or structures in a health care organization that significantly impact safety and/or quality care • Surveyors use the priority CFAs to: • Review supporting data • Plan on-site survey activity • Plan tracer focus areas and potential relevant standards
Critical Focus Areas include: • Assessment and Care • Communication • Competency and Credentialing • Equipment Use • Infection Control • Information Management • Medication Use • Organization Structure • Orientation and Training • Rights and Ethics • Physical Environment • Quality Improvement Expertise and Activity • Patient Safety • Staffing
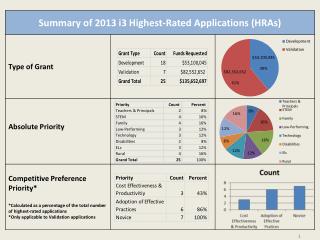
EXAMPLE: Top Critical Focus Areas for ABC Medical Center, January 2004 Critical Focus Areas Critical Focus Areas are defined as processes, systems or structures in a healthcare organization shown to be necessary to patient safety and quality care. Your organization’s prioritized Critical Focus Areas (and definitions for those areas) are: Care and Assessment • Determination of what kind of care is required to meet a patient's initial needs as well as his or her needs as they change in response to care. Also, includes re-assessment and discharge planning needs. Communication • A process in which information is exchanged between individuals and departments. Communication includes an organization's policies and procedures - as a mechanism to communicate with staff. Staffing • Providing the correct number, skill mix, and trained (competency) resources to meet the needs of patients. Staffing includes employees who are the direct and indirect caregivers at the health care organization. Patient Safety • Limiting the risk an intervention (e.g., use of a drug or a procedure) and the care environment have for a patient.
Priority Focus Process: Outputs – Clinical Service Groups • PFP display an organization’s priority Clinical Service Groups (CSGs) • Clinical Service Groups are groups of patients in distinct, clinical populations for which data are collected • Surveyors use the priority CSGs to: • Identify clinical service groups for focus • Use organization’s active patient list and identified clinical service groups to select tracer patients
EXAMPLE: Top Clinical Service Groups for ABC Medical Center, January 2004 Clinical Service Groups Clinical Service Groups are categories of patients/clients into distinct groups for use in the Priority Focus Process. Your organization’s prioritized Clinical Service Groups are: • Cardiology • General Surgery • Orthopedic • Rehab
Priority Focus Process: Outputs – On-Site Survey Activities • Information from the prioritized Critical Focus Areas and Clinical Service Groups are used to help guide the focus of on-site survey activities such as: • Leadership Conference • Systems Tracer: Data Use • Systems Tracer: Infection Control • Systems Tracer: Medication Management • Patient/client/resident tracers
Priority Focus Process Goals . . . • The goal of the Priority Focus Process (PFP) • Modify the on-site survey process by providing consistent focus on issues most relevant to patient safety and quality of care specific to the HCO • Provide the process and infrastructure to: • Convert pre-survey data into information that focuses on-site survey activities (consistency) • Position the Joint Commission to customize the accreditation process (specificity)
Priority Focus ProcessContent Development • In order to develop the PFP, JCAHO did research and conducted focus groups to identify data that are associated with priority issues – these issues were defined as critical focus areas • JCAHO developed categories for sorting services – these are called clinical service groups • JCAHO then identified a process to obtain these data from multiple sources, and to use automation to sort the data • These data are then used in the PFP
Sources Blomme, Jane (2002) ppt. Shared Visions – New Pathways: Sharpening the focus of the accreditation process on care systems critical to the safety and quality of care. Joint Commission on Accreditation of Health Care Organizations. Massaro, Russ (May 2003) ppt. Executive Briefings, JCAHO Shared Visions—New Pathways: 2004 Accreditation Process, Joint Commission on Accreditation of Health Care Organizations. SMART: Staff Maintaining Accreditation Readiness Together (2003) ppt. Shared Visions – New Pathways: Update on the Survey of the Future. Inova Health System.