Calvin Cycle and Photorespiration
E N D
Presentation Transcript
1. Calvin Cycle and Photorespiration
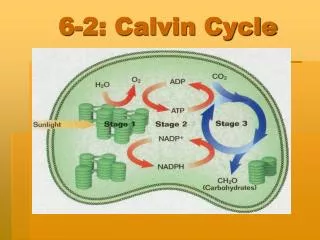
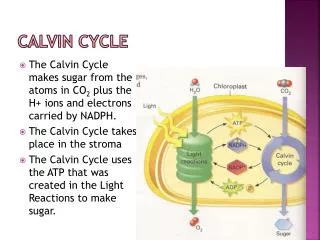
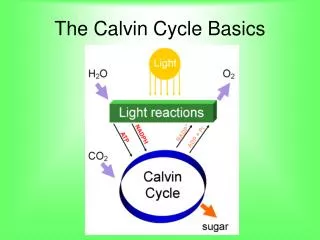
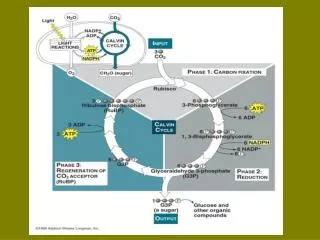
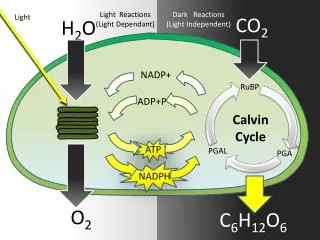
2. Calvin Cycle Where does the Calvin Cycle occur?
In the stroma
What goes into the Calvin Cycle?
ATP, NADPH, Carbon Dioxide
What comes out of the Calvin Cycle?
Sugar, ADP, NADP+
7. Rate of Photosynthesis What is a rate?
It is the activity per unit time.
What factors can affect the photosynthetic rate?
8. Light Intensity
9. The Effect of Light Intensity on Photosynthetic Rate
10. Temperature
11. The Effect of Temperature on Photosynthetic Rate
12. The Effect of Light Intensity and Temperature on Photosynthetic Rate
13. Oxygen Concentration
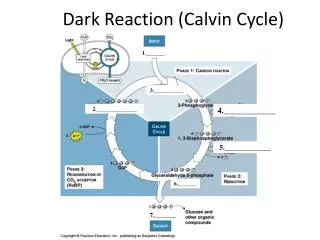
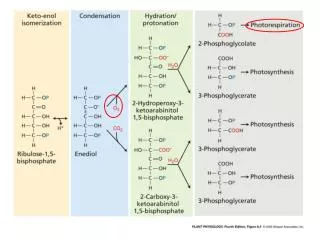
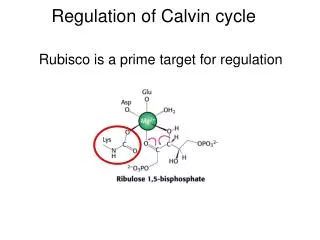
14. Why Does Oxygen Effect Photosynthetic Rate? What is the role of rubisco?
Rubisco incorporates carbon dioxide into the RuBP during the Calvin cycle.
Rubisco, however, has an active site that accommodates both oxygen and carbon dioxide.
What happens when rubisco incorporates oxygen into the RuBP molecule?
16. Photorespiration The overall rate of photosynthesis decreases.
Both photorespiration and photosynthesis occur at the same time
17. Conditions for Photorespiation What conditions will lead to a lot of photorespiration?
Hot
Dry
Sunny
What happens to stomates under such conditions?
They close.
19. Evolution Why does rubisco bind both oxygen and carbon dioxide?
When Calvin Cycle evolved there was little oxygen in the atmosphere.
20. Solutions What solutions have some plants found for this problem?
C4 Pathway.
Sugarcane, corn, crabgrass have all evolved a different structure that minimizes photorespiration.
23. C3 vs. C4 plants When do C4 plants outcompete C3 plants?
Under the hot, dry, sunny conditions that favor photorespiration.
C4 plants have evolved in these hot, warm climates.
What happens to acid levels in a C4 plant, as compared to a C3 plant during the day?
24. CAM Plants At night, stomata open, take in CO2, incorporate it into organic acids and store those acids in vacuoles until daylight
during the day, stomates close
The organic acids stored at night, break down, release CO2 and rubisco incorporates it into sugar.
26. C4 plants use a new structure to solve the photorespiration problem.
CAM plants use time to solve the photorespiration problem.