Network Protocols
370 likes | 599 Vues
Network Protocols. Chapter 8. Chapter Objectives. List the different types of network protocols Identify the working of each network protocol Explain the functions of different protocols in TCP/IP protocol suite Configure IPX/SPX on Windows XP Install NetBIOS/NetBEUI on Windows XP.

Network Protocols
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Network Protocols Chapter 8
Chapter Objectives • List the different types of network protocols • Identify the working of each network protocol • Explain the functions of different protocols in TCP/IP protocol suite • Configure IPX/SPX on Windows XP • Install NetBIOS/NetBEUI on Windows XP
Recall • MAC address is a hardware address that is permanently embedded into NIC • When two nodes are connected by directly connecting cables, it is called direct cable connection • Two types of volt-ohm meters: • Analog • Digital • Function of a probe is to trace signal emitted by the tone generator
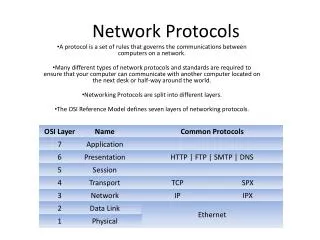
Introducing Protocols • Set of predefined rules used by devices in network for data transfer • Network Protocols: • NetBIOS/NetBEUI • TCP/IP • ARP/RARP • ICMP/IGMP • UDP • IPX/SPX • HDLC/SDLC
NetBIOS/NetBEUI • Network Basic Input/Output System (NetBIOS) used for communication within LAN • Operates at Transport and Session layers of OSI model • NetBIOS Extended User Interface (NetBEUI) adds capabilities to NetBIOS and an advanced version of NetBIOS • Widely used in Ethernet, Token Ring and Windows NT networks
NetBIOS Services • NetBIOS Name Service is implemented in Microsoft Windows as Windows Internet Name Service (WINS).
Name Service • Implemented in Microsoft Windows as Windows Internet Name Service (WINS). • Provides means to application to register its NetBIOS name • Name Service functions include • Add Name • Add Group Name • Delete Name • Find Name
Session Service Establishes session for data exchange between computers using TCP port 139 Session Termination Process Session Establishment Process
Datagram Service • Uses the UDP port 138 and provides a connectionless and broadcast-oriented data communication between two devices. • Divides data in datagrams before sending • Datagram service functions include: • Send Datagram • Send Broadcast Datagram • Receive Datagram • Receive Broadcast Datagram
NetBIOS Name Resolution • Used to map NetBIOS names to IP addresses • Methods used to resolve names: • NetBIOS Name Cache • NetBIOS Name Server (NBNS) • Local Broadcast • Order of resolving names depends on node types: • B-node (broadcast) • P-node (peer-peer) • M-node (mixed) • H-node (hybrid)
NetBEUI • Enhanced version of NetBIOS • NetBIOS is used in Ethernet and Win NT where as NetBEUI is used in Win 95, Win 98 and LAN • Uses unacknowledged connectionless mode for name service and datagram service • Uses virtual circuit approach for session service • NetBEUI provides name service, datagram service and session service
TCP/IP • Two layer communication protocol used by Internet • TCP provides connection-oriented reliable transport service • Divides the message into smaller packets called segments • IP is a connectionless and unreliable datagram protocol and provides no error checking • IP transfers data in the form of packets called datagrams
TCP/IP Protocol Suite • Designed before OSI model • Consists of five layers • Provides independent protocols at each layer
IP Datagram Fragmentation • Fragmentation refers to breaking datagrams into pieces • Maximum Transfer Unit (MTU) is maximum amount of data that frame can carry • Datagram is fragmented when its size exceeds MTU of network • Fragments follow different paths to reach destination
ARP/RARP • To deliver packet both physical and logical addresses are necessary • Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) provides physical address when logical address is known • Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) maps logical address to physical address • RARP is useful when device is booted for first time
ICMP/IGMP • Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) provides error reporting and query management mechanism • ICMP handles problems occurring while packet transmission • Internet Group Message Protocol (IGMP) manages multicasting and group membership of devices
ICMP Message Types ICMP Messages Error Reporting Query Destination Unreachable Echo request and reply Source Quench Timestamp request and reply Time Exceeded Address Mask Request and reply Parameter Problem Router Solicitation and Advertisement Redirection
UDP • User Datagram Protocol (UDP) provides connectionless process-to-process communication • UDP packets are called user datagrams. • User Datagram Format:
UDP Operation - I Encapsulation Decapsulation
UDP Operation - II Server Queue Client Queue
IPX/SPX • Novell NetWare system uses IPX/SPX as communication protocol within networks • IPX operates at Network layer for connectionless communication • SPX operates at Transport layer for connection-oriented communication • Together, IPX/SPX provides same services as TCP/IP
IPX/SPX Naming Conventions • IPX/SPX/NetBIOS Compatible Transport Protocol (NWLink) uses two types of IPX network numbers for routing purposes: • Internal network number – Mentioned as Internal network number in NWLink IPX/SPX/NetBIOS Compatible Transport Protocol Properties dialog box • External network number – Mentioned as Network number in Manual Frame Detection dialog box
HDLC/SDLC • High Level Data Link Control (HDLC) and Synchronous Data Link Control (SDLC) are bit-oriented synchronous protocols in which data frames are interpreted as series of bits • Both are useful for half-duplex and full-duplex communication • Windows XP still support DLC
HDLC Nodes and Configurations • Types of HDLC nodes are: • Primary Station • Secondary Station • Combined Station • Supported link configurations: • Unbalanced • Balanced
HDLC Data Transfer Modes • Normal Response Mode (NRM) – Secondary station requires permission from primary station before sending data • Asynchronous Response Mode (ARM) – Secondary station can transfer without permission from primary station • Asynchronous Balanced Mode (ABM) – Either of the combined station can initiate the transmission
SDLC • Bit-oriented protocol and similar to HDLC • Only primary and secondary stations are used
Summary - I • Network protocols are the set of predefined rules, used by the devices connected to network to communicate with each other • Different network protocols include NetBIOS/NetBEUI, TCP/IP and IPX/SPX • NetBIOS protocol is used for communication within a LAN and operates at the session layer of the OSI model • NetBIOS provides three types of services namely Name service, Session service and Datagram service • Name service allows an application to register its NetBIOS name in the network
Summary - II • Two computers can establish a session for data transfer using the Session service which is a connection-oriented service • In the connectionless Datagram service, data is transferred in the form of small packets called datagrams • NetBIOS name resolution is used to map a NetBIOS names to an IP address. Methods used for resolution are, NetBIOS Name Server (NBNS), NetBIOS name cache and Local Broadcast • LMHOSTS file is a static file that resolves the names to IP address for applications running on the remote computer • TCP/IP is a five-layer protocol suite developed before the OSI model
Summary - III • TCP is a connection-oriented, reliable and process-to-process transport layer protocol in the TCP/IP protocol suite • At TCP, data is divided into segments with each segment having sequence number for reassembly of the data at the destination • Connection establishment requires three-way handshaking; connection termination requires four-way handshaking process • IP is an unreliable connectionless protocol responsible for source-to-destination delivery • Packets in the IP layer are called datagrams which consist of data and header
Summary - IV • Fragmentation is the division of a datagram into smaller units when size of the datagram exceeds MTU • ARP protocol is used to obtain the physical address of the device when its logical address is known • RARP protocol is used to obtain the logical address of the device when its physical address is known • ICMP protocol is used to send error and control messages. Two types of ICMP messages are Error-reporting messages and Query messages • Error reporting messages include Destination Unreachable, Source Quench, Time exceeded, Parameter Problem and Redirection
Summary - V • Query messages include Echo Request and Reply, Timestamp Request and Reply, Address Mask Request and Reply and Router Solicitation and Advertisement • IGMP protocol is used to govern the management of multicast groups in a network. Three types of IGMP messages are Query, Membership Report and Leave Report • UDP protocol operates at the transport layer and provides connectionless and unreliable service • The UDP packet is called as user datagram which is encapsulated into an IP packet • Incoming and outgoing queues hold messages going to and from UDP
Summary - VI • Novell NetWare operating system uses IPX/SPX protocol for communication within a network • IPX operates at the network layer and provides connectionless routing services using either RIP or NLSP • HDLC is a data link control protocol used for point-to-point communications over a serial links • Three types of devices used in HDLC are primary station, secondary station and combined station • HDLC supports three configuration modes: Normal Response Mode, Asynchronous Response Mode and Asynchronous Balanced Mode