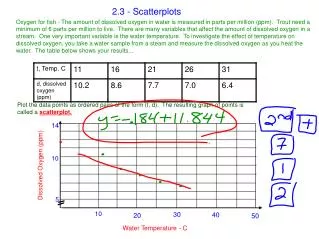
(2.3) Polynomial Functions and Their Graphs
210 likes | 688 Vues
(2.3) Polynomial Functions and Their Graphs. Identifying End Behavior Finding x-intercepts Using the Intermediate Value Theorem Graphing Polynomial Functions. End Behavior. Leading Coefficient. End Behavior. Best Graph Description. End Behavior. Example. Degree. Up Right.

(2.3) Polynomial Functions and Their Graphs
E N D
Presentation Transcript
(2.3) Polynomial Functions and Their Graphs Identifying End Behavior Finding x-intercepts Using the Intermediate Value Theorem Graphing Polynomial Functions
End Behavior Leading Coefficient End Behavior Best Graph Description End Behavior Example Degree Up Right Line with a Positive Slope Odd Positive Down Left Down Right Line with a Negative Slope Odd Negative Up Left
End Behavior Leading Coefficient End Behavior Best Graph Description End Behavior Example Degree Quadratic with a Positive Coefficient Up Right Even Positive Up Left Down Right Quadratic with a Negative Coefficient Even Negative Down Left
Identifying End Behavior Odd Positive Up Right; Down Left Even Negative Down Right; Down Left Even Positive Up Right; Up Left Down Right; Up Left Odd Negative
Analyzing Zeros (x-intercepts) x-intercept behavior Graphic Representation Multiplicity Graph goes THROUGH the x-intercept Odd Multiplicity Graph TURNS at the x-intercept Even Multiplicity
Finding and Analyzing x-intercepts Multiplicity of Two Goes Through the x-axis at x-intercept -2 Turns at the x-axis at 2
Finding and Analyzing x-intercepts Multiplicity of Two Goes Through the x-axis at x-intercept -5 Turns at the x-axis at x-intercepts -5 and -1
Intermediate Value Theorem for Polynomials Take f(a) and f(b). If there is a sign change between the two values then there exists a zero between a and b.
Using the Intermediate Value Theorem Sign changes so there IS a zero (x-intercepts) between x = 0 and x = 1
Using the Intermediate Value Theorem Sign changes so there IS a zero (x-intercepts) between x = 1 and x = 2
Graphing Polynomial Functions • Leading Coefficient Test:Analyze the end behavior. (Ex: #’s 1-4) • Find the x-intercepts:Solve the polynomial and analyze the zeros. (Ex: #’s 5-6) • Find the y-intercept:Substitute 0 in for x • Determine the symmetry:Is the function even (y-axis symmetry), odd (origin) symmetry, or neither. • Find a few addition points and turning points:Use a table of values if needed. The maximum number of turning points will be 1 LESS THAN THE DEGREE of the polynomial.
Odd Negative Down Right; Up Left Graph goes THROUGH x-intercepts 0 and 3
y 2 -1 x 1 -2
Odd Negative Down Right; Up Left Graphgoes THROUGH x-intercept 2and TURNS at x-intercept -2
y 1 -1 x 1 -1
Even Positive Up Right; Up Left Graphgoes THROUGH x-intercepts -5 and 3and TURNS at x-intercept -1
y 1 -1 x 1 -1