Enthalpy Change of Methanol Formation from Methane and Oxygen
10 likes | 149 Vues
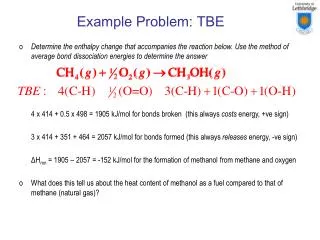
This problem involves calculating the enthalpy change (ΔHrxn) for the reaction between methane and oxygen to form methanol using average bond dissociation energies. The bonds broken cost energy (positive sign) and include 4 C-H and 0.5 O=O, totaling 1905 kJ/mol. The bonds formed release energy (negative sign), including 3 C-H, 1 C-O, and 1 O-H, totaling 2057 kJ/mol. The final calculation shows ΔHrxn = 1905 - 2057 = -152 kJ/mol, indicating methanol's greater heat content as a fuel compared to methane.

Enthalpy Change of Methanol Formation from Methane and Oxygen
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Example Problem: TBE • Determine the enthalpy change that accompanies the reaction below. Use the method of average bond dissociation energies to determine the answer 4 x 414 + 0.5 x 498 = 1905 kJ/mol for bonds broken (this always costs energy, +ve sign) 3 x 414 + 351 + 464 = 2057 kJ/mol for bonds formed (this always releases energy, -ve sign) ΔHrxn = 1905 – 2057 = -152 kJ/mol for the formation of methanol from methane and oxygen • What does this tell us about the heat content of methanol as a fuel compared to that of methane (natural gas)?