Metallic Crystal Structures
310 likes | 807 Vues
Metallic Crystal Structures. Rajapalayam Rajus’ College Dr.S.Somasekaran. Basics of crystal Structure. An ideal crystal is a periodic array of structural units, such as atoms or molecules. It can be constructed by the infinite repetition of these identical structural units in space.

Metallic Crystal Structures
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Metallic Crystal Structures Rajapalayam Rajus’ College Dr.S.Somasekaran
Basics of crystal Structure • An ideal crystal is a periodic array of structural units, such as atoms or molecules. • It can be constructed by the infinite repetition of these identical structural units in space. • Structure can be described in terms of a lattice, with a group of atoms attached to each lattice point. The group of atoms is the basis.
Bravais Lattice • An infinite array of discrete points with an arrangement and orientation that appears exactly the same, from any of the points the array is viewed from. • A three dimensional Bravais lattice consists of all points with position vectors R that can be written as a linear combination of primitive vectors. The expansion coefficients must be integers.
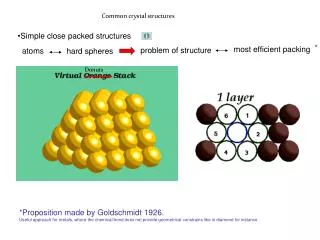
Materials and Packing • Crystalline materials... • atoms pack in periodic, 3D arrays metals -many ceramics -some polymers crystalline SiO2 Noncrystalline materials... atoms have no periodic packing complex structures -rapid cooling noncrystalline SiO2
Primitive Unit Cell • A primitive cell or primitive unit cell is a volume of space that when translated through all the vectors in a Bravais lattice just fills all of space without either overlapping itself or leaving voids. • A primitive cell must contain precisely one lattice point.
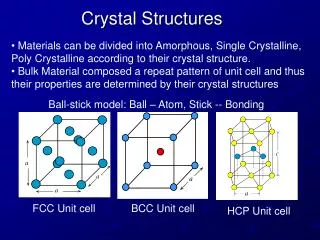
Simple Cubic Structure (SC) • Rare due to low packing density (only Po has this structure) • Close-packed directions are cube edges. Coordination # = 6 (# nearest neighbors)
Atomic Packing Factor (APF) • APF = Volume of atoms in unit cell • Volume of unit cell • • APF for a simple cubic structure = 0.52
Atomic Packing Factor: BCC a 3 a 2 Close-packed directions: R 3 a length = 4R = a atoms volume 4 3 p ( 3 a/4 ) 2 unit cell atom 3 APF = volume 3 a unit cell • APF for a body-centered cubic structure = 0.68 a Adapted from Fig. 3.2(a), Callister & Rethwisch 8e.
Face Centered Cubic Structure (FCC) • Atoms touch each other along face diagonals. --Note: All atoms are identical; the face-centered atoms are shaded differently only for ease of viewing. ex: Al, Cu, Au, Pb, Ni, Pt, Ag • Coordination # = 12 Adapted from Fig. 3.1, Callister & Rethwisch 8e. Click once on image to start animation 4 atoms/unit cell: 6 face x 1/2 + 8 corners x 1/8 (Courtesy P.M. Anderson)
Hexagonal Close-Packed Structure (HCP) A sites Top layer c Middle layer B sites A sites Bottom layer a • ABAB... Stacking Sequence • 3D Projection • 2D Projection Adapted from Fig. 3.3(a), Callister & Rethwisch 8e. 6 atoms/unit cell • Coordination # = 12 ex: Cd, Mg, Ti, Zn • APF = 0.74 • c/a = 1.633
nA VCNA Mass of Atoms in Unit Cell Total Volume of Unit Cell = Theoretical Density, r Density = = where n = number of atoms/unit cell A =atomic weight VC = Volume of unit cell = a3 for cubic NA = Avogadro’s number = 6.022 x 1023 atoms/mol
Miller indices of lattice plane • The indices of a crystal plane (h,k,l) are defined to be a set of integers with no common factors, inversely proportional to the intercepts of the crystal plane along the crystal axes: