Ch. 15 IDs
260 likes | 445 Vues
Ch. 15 IDs. 1.) Ellis Island. What – Immigrant inspection station Where – New York City, NY When – 1892-1954 Significance – Major center for immigration for those travelling across the Atlantic. 2.) Angel Island. What – Immigrant inspection station Where – San Francisco, CA

Ch. 15 IDs
E N D
Presentation Transcript
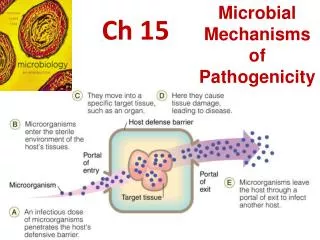
1.) Ellis Island • What – Immigrant inspection station • Where – New York City, NY • When – 1892-1954 • Significance – Major center for immigration for those travelling across the Atlantic
2.) Angel Island • What – Immigrant inspection station • Where – San Francisco, CA • When– 1910-1940 • Significance - Major center for immigration for those travelling across the Pacific
3.) Working Man’s Party/Chinese Exclusion Act • What – Political Party that tried to stop Chinese immigration/law that stopped Chinese immigration • When – Law was into effect from 1882-1943 • Where – WMP was centrally located in CA • Significance – Shows the racial intolerance of the time period
4.) Skyscraper • What – Tall, large building • When – Disputed b/w 1870 and 1885 • Significance – Changed the layout and look of urban cities (Leads to birth of modern city)
5.) Urbanization • What – Process of people moving to and building cities • Significance – Urbanization leads to a number of problems, which people will then call for reform
6.) Mass Transit Systems • What – Urban transportation systems including subways, cable cars, trolleys, and elevated trains • Significance – Allows middle class families to move away from the cities to the suburbs and commute to work
7.) Boll Weevil • What – Insect that feeds on cotton • Significance – Boll weevil ruins many crops for southern farmers, causing them to move north and look for jobs in industries
8.) Great Chicago Fire • What – Fire • Where – Chicago, IL • When – 1885 • Significance – • 1.) Destroys nearly 20% of the city, leaving 100,000 homeless • 2.) Causes city officials to create and enforce fire safety/prevention programs
9.) Nativism • What – Movement/feeling of hatred towards immigrants and favoritism toward those born within country • Significance – Movement will lead toward changes in legislation that banned immigration from certain countries
10.) Political Machine • What – term used to describe a political party that dominates politics on it’s level (city/state/regional) • Significance – People go along with political machines because the politicians usually provide people with the services that they need
11.) Tammany Hall • What – Political Machine (Democrat) • Where – New York City, NY • When – 1854-1932 • Significance – Greatest example of a political party in American History
12.) Gilded Age • What – Term used to describe period in American History that saw great prosperity, industrialization, urbanization, political corruption, and reform • When – 1870s-1920s • Who – Coined by Mark Twain • Significance – Era in which one sees the birth of modern America
13.) Horatio Alger • Who – Famous novelist • Significance – His “rags to riches” novels helped portray the popular theory of individualism
14.) Social Darwinism • What – Theory that some cultures/nations are better than others • Significance – Theory is used as justification for US government and political decisions of the era
15.) Gospel of Wealth • What – Movement lead by wealthy philanthropists in which they thought it was their duty to make contributions to society • When – Gilded Age • Significance – Will lead to the creation of beloved public institutions such as libraries, museums, and theatres
16.) Realism • What – Cultural movement that focused on portraying society as realistically as possible • When – Gilded Age • Significance – Portrays social problems to society, who in turn will call for reform
17.) Mark Twain • Who – Famous writer • Significance – • 1.) Coins the term “Gilded Age” • 2.) Famous realist and satirist/social critic • 3.) Author of The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn
18.) “Rise of Popular Culture” • What – Time period in which people living in cities were making more money and had more free time to spend it • When – Gilded Age • Significance – Leads to new ways to spend leisure time, including professional sports, vaudeville shows, and saloons
19.) Social Gospel • What – Christian movement that focused on using Christian principles on making social improvements • When – Gilded Age • Significance – Credited with starting inner city missions
20.) Henry George • Who – Author and early reformer • When – Gilded Age • Significance – His thoughts and ideas will lead to inspiring a generation of reformers during the Progressive Era
21.) Salvation Army/YMCA • What – Organizations created in order to help provide for the poor and struggling classes in the inner cities • Significance – One of the first social welfare programs
22.) Morrill Land Act • What – Legislation that set land aside for the creation of state colleges • When– 1862/1890 • Significance – • 1.) Expansion of act in 1890 was geared toward southern states and mid-western states • 2.) Southern states created two colleges (white/black) • 3.) Leads to creation of some of the greater high education institutions in US
23.) Naturalism • What – Cultural movement that focused on nature • Significance – Naturalists challenged technology and reminded people that nature will always prevail over human efforts
24.) Public Education • What – During this time period, more public schools were created, as well as compulsory school laws • When – Gilded Age • Significance – Schools taught discipline, vocational skills, English, history and civics in order to “create” good citizens and workers
25.) Settlement House Movement • What – Centers created in inner cities that provided services to people such as food and shelter, English classes, classes that taught skills • When – Gilded Age • Significance – Credited as the birth of social work