Chronology
60 likes | 218 Vues
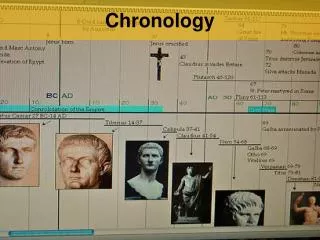
Chronology. chronos – time logos – study of, order of. Terminology. BCE = before the common era (formerly BC) CE = in the common era (formerly AD, anno domini ) Year “zero” is not just the birth of Christ New terminology is more inclusive. Points to Remember.

Chronology
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chronology chronos – time logos – study of, order of
Terminology • BCE = before the common era (formerly BC) • CE = in the common era (formerly AD, anno domini) • Year “zero” is not just the birth of Christ • New terminology is more inclusive.
Points to Remember • 2000 BCE occurs before 1000 BCE but 1000 CE occurs before 2000 CE. • The fifth century BCE is 499 – 400 BCE. • The first millennium BCE is 999 – 0 BCE. • First quarter of the fifth century BCE is 499 – 475 BCE. Second quarter of the fifth century BCE is 475 – 450 BCE, etc.
Art Historical/Historical Terms • Terms like Paleolithic, Assyrian, Classical, Roman Imperial refer both to an artistic style (the definition of which is often changing) and a specific time period. • Terms imply a change in civilization or culture. • Paleolithic, the “old stone age” refers to a nomadic culture with a certain level of technological experience. Neolithic, the “new stone age” refers to a more settled culture with domestic agriculture and herding with a different level of technological experience.
How do we determine DATE • Relative dating • Comparison to other objects that have a secure date. • Historical records, archaeological finds secure the date. • Absolute dating • Scientific methods – radiometric dating (C-14), thermoluminescence, electron spin resonance (ESR). • Works on materials that are more than 5000 years of age and less than 40,000 years of age.
Memorization of Dates • In this class, you need to memorize dates. • Dates are often civilization specific. • e.g. Bronze Age in the British Isles and parts of France refers to the dates 2300 – 1000 BCE. In Greece and the Mediterranean, the Bronze Age begins sooner – 3000 – 1000 BCE.