Mitosis
220 likes | 281 Vues
Explore the intricate process of mitosis, from duplication of DNA to formation of daughter cells. Understand key phases like prophase, anaphase, and cytokinesis, and the role of mitotic spindles. Learn about cell cycle regulation, checkpoints, and the impact of cancer on this vital process.

Mitosis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Mitosis AP Biology Crosby High School
Cell Division • Reproduction, Growth, and Repair • Basic steps: • Duplicates DNA • Copies split to opposite ends • Cell splits • 2 Daughter Cells formed
Genome • Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote • Prokaryote: Single strand of DNA • Eukaryote: • More than on strand of DNA • Each species has a specific number of chromosomes • Human Somatic Cells: 46 chromosomes (Diploid) • Human Gametic Cells: 23 chromosomes (Haploid)
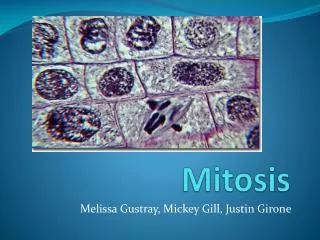
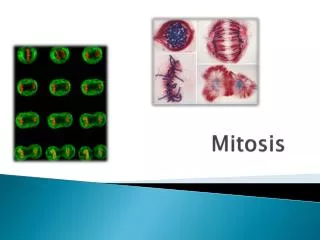
Structures and Overview of Splitting • DNA strand wrapped around proteins • Chromatin: DNA/Protein complex • Condenses to form Chromosomes • Copied forming Sister Chromatids • Chromatids joined at Centromere • Chromatids separate in Mitosis • Cytoplasm separates in Cytokinesis
Interphase • 90% of Cell Cycle • Consists of Three Phases • G1 Phase (Gap one) • Growth of the cell • S Phase (Synthesis) • Growth of the cell • DNA replication • G2 Phase (Gap two) • Growth of the cell
Mitotic Phase • “Please Pour Me Another Tequila” • Prophase • Prometaphase • Metaphase • Anaphase • Telephase
Mitotic Spindle • Centrosomes form spindles • Centriole pairs inside Centrosomes • Centrosomes replicate near nucleus • Two centrosomes grow spindle microtubules • Separate to opposite ends of the cell • Spindles “play tug-o-war” at Kinetochores • Pull both directions until chromosomes reach metaphase plate
Mitotic Spindles and Anaphase • Proteins holding sister chromatids deactivate • Chromosomes “walk” along microtubules • Microtubules shorten by depolymerizing • Nonkinetochore microtubules lengthen the cell
Cytokinesis • Begins with Cleavage furrow • Actin and Myosin contraction • Differences of Plant Cytokinesis • Vesicles from Golgi form cell plate • Plate grows and fuses with plasma membrane • Cell wall materials accumulate and form cell wall
Mitosis: Evolution of Binary Fission? • Prokaryotes have no spindle fibers • Origin of Replication replicates in opposite directions • Plasma membrane grows inward • Dinoflagellates and Diatoms • Unicellular algae • Divides with nuclear envelope intact
Cell Cycle Regulation • Controlled on the molecular level by signals • Fused cells could force Mitosis • Fused to have two nuclei • Performed same function • Cell cycle control system • Internal signals • External signals
Cell Cycle Checkpoints • 3 major checkpoints • G1(Restriction point) • Begins the S phase • Decides whether the cell will divide or not • Yes: Enters S phase • No: Enters G0 phase • G2 • Precedes mitosis • M • Has mitosis completed?
Cyclin and Cyclin Dependent Kinases • Cyclin • Fluctuates in the cell • When present bind to Cdks for activation • G1 checkpoint contains 3 Cdks and several cyclins • Maturation Promoting Factor (MPF) • Past G2 • Initiates Mitosis by phosphorylating proteins • Turns itself off by degrading cyclin • Remains present in inactive form
Internal Signals • Messages received from Kinetochores • Anaphase does not begin until all kinetochores are attached to a spindle fiber • Signal comes from non-attached • Anaphase promoting complex (APC) inactive • Active: APC triggers breakdown of cyclin and deactivation of sister chromatids
External Signal • Platelet-derived Growth Factor (PDGF) • Fibroblasts have PDGF receptors • Heals wounds • Density dependent Inhibition • Cells form one layer IN CULTURE and stop • Continue to grow when cells are removed • Anchorage Dependence • Must be attached to substratum
Cancer • Uncontrolled cell growth • Control point malfunctions • Cell continues to grow beyond inhibition • HeLa cells have been growing since 1951
Onset of Cancer • Transformation: cell malfunctions • If not destroyed it becomes a tumor • Benign: Remains at origin • Malignant: invasive enough to impair organs • Cells lose function and inhibition • Cells lose attachment and spread • Spread through lymphatic or blood vessels • Metastasis