Resolving Many to Many Relationships
50 likes | 317 Vues
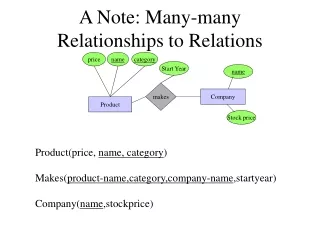
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Objectives. Identify the need for an intersection entityCreate an intersection entityCreate a UID for the new entity. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Identifying the Problem. . . . . . . . TITLE. SUPPLIER. supplied by. supplier of. In which e

Resolving Many to Many Relationships
E N D
Presentation Transcript
1. Resolving Many to Many Relationships Data Modeling and Relational Database Design Lesson Preparation
This session is about creating intersection entities. There are two practices. Make sure you are fully conversant with the solutions and are able to discuss them with the students.
Lesson Controls
It is a short lesson but encourage interaction from the students.
Timings
Lesson 15 minutes
Practice 30 minutes
Intended as the second lesson on the second morning.
Practice Controls
Discuss the results of practice 7-1 before moving on to 7-2.Lesson Preparation
This session is about creating intersection entities. There are two practices. Make sure you are fully conversant with the solutions and are able to discuss them with the students.
Lesson Controls
It is a short lesson but encourage interaction from the students.
Timings
Lesson 15 minutes
Practice 30 minutes
Intended as the second lesson on the second morning.
Practice Controls
Discuss the results of practice 7-1 before moving on to 7-2.
2. Objectives Identify the need for an intersection entity
Create an intersection entity
Create a UID for the new entity
3. Identifying the Problem Technical Notes
The first question means that the business using this model could not extract a specific instance in answer to the question.
The second question shows that an attribute cannot be stored sensibly in either entity. It is actually an attribute of the relationship.
Either reason gives rise to the need for a new entity holding information specific to which SUPPLIER supplied an instance of TITLE and which TITLE was supplied by which instance of SUPPLIER.
Class Management
This slide is intended to help you discuss WHY you need to resolve many to many relationships.
Ask them what the new entity should be called. suggest that if it doesn�t actually exist in the real world then a combination of the names of the two masters separated by a �/�, is an acceptable alternative.Technical Notes
The first question means that the business using this model could not extract a specific instance in answer to the question.
The second question shows that an attribute cannot be stored sensibly in either entity. It is actually an attribute of the relationship.
Either reason gives rise to the need for a new entity holding information specific to which SUPPLIER supplied an instance of TITLE and which TITLE was supplied by which instance of SUPPLIER.
Class Management
This slide is intended to help you discuss WHY you need to resolve many to many relationships.
Ask them what the new entity should be called. suggest that if it doesn�t actually exist in the real world then a combination of the names of the two masters separated by a �/�, is an acceptable alternative.
4. Intersection Entities Technical Notes
The intersection entity has a many to one relationship with both it�s masters.
Class Management
Point out that when an M:M is resolved a further M:M may be uncovered which must also be resolved.
Technical Notes
The intersection entity has a many to one relationship with both it�s masters.
Class Management
Point out that when an M:M is resolved a further M:M may be uncovered which must also be resolved.
5. Unique Identifiers Technical Notes
The UID for an intersection entity may already exist in the business, in the example every item in the catalog has a unique number so that could be used. If it doesn�t exist in the business then a common alternative is to use a combination of the relationships.
Class Management
Make sure that they understand that should NOT invent a UID. If it exists in the business then it should be used, if it does not then a combination of relationships should be used.
In logical design, for technological reasons it may be felt that the foreign keys are not suitable for a primary key so a surregate key may be created. It is not a business need however.Technical Notes
The UID for an intersection entity may already exist in the business, in the example every item in the catalog has a unique number so that could be used. If it doesn�t exist in the business then a common alternative is to use a combination of the relationships.
Class Management
Make sure that they understand that should NOT invent a UID. If it exists in the business then it should be used, if it does not then a combination of relationships should be used.
In logical design, for technological reasons it may be felt that the foreign keys are not suitable for a primary key so a surregate key may be created. It is not a business need however.
6. Summary Identify the need for an intersection entity
Create an intersection entity
Create a UID for the new entity