Understanding Photosynthesis: Processes, Reactions, and Pathways in Plants
110 likes | 249 Vues
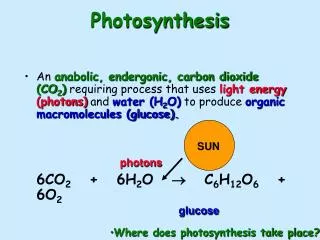
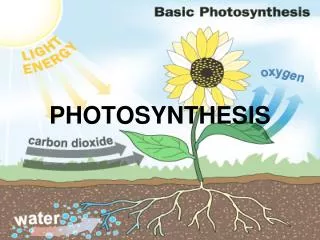
Photosynthesis is a vital process occurring in the chloroplasts of plants, primarily within thylakoids and the stroma. The overall reaction can be summarized as 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2. The process consists of light-dependent reactions where sunlight is absorbed to produce oxygen, ATP, and NADPH, and the Calvin cycle, utilizing ATP and NADPH to create organic compounds like glucose. Factors such as light intensity, CO2 levels, and temperature can impact photosynthesis rates, and variations like the C4 and CAM pathways help plants adapt to different climates.

Understanding Photosynthesis: Processes, Reactions, and Pathways in Plants
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Photosynthesis -Primarily in chloroplasts of plants -Reactions occur inside structures within the chloroplasts called thylakoidsand the stroma.
Chloroplast Single thylakoid Granum Stroma
Overall Reaction of Photosynthesis Reactants: carbon dioxide, water, and energy (sun) Products: glucose and oxygen 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2
Light Reactions Function: -Energy from the sun is absorbed by chlorophyll located inside the thylakoids. -The light energy is transferred from the chlorophyll to NADP+ to form NADPH. This occurs in a series of reactions called the electron transport chain (ETC) across the thylakoid membrane. -ATP is formed from ADP by chemiosmosis across the thylakoid membrane. (ADP adds a P group with the help of the protein ATP Synthase.) Location: chlorophyll & thylakoid membrane Reactants: H2O, energy (sun) ADP, and NADP+. Products: oxygen, ATP, and NADPH.
Photosynthesis H2O CO2 Light NADP+ ADP+ P Light- dependent reactions Calvin cycle Sugars O2
Calvin Cycle (Dark Reactions) Function: -No sunlight is needed. -Plants use the energy within ATP and NADPH to build organic compounds (glucose) which are sources of nutrients for the plant. Location: stromaof the chloroplast Reactants: CO2 (from air), ATP and NADPH Products: Organic Compounds (Glucose)
Photosynthesis H2O CO2 Light NADP+ ADP+ P Light- dependent reactions Calvin cycle Sugars O2
Photosynthesis • The two sets of photosynthetic reactions work together. • The light-dependent reactions trap sunlight energy in chemical form. • The light-independent reactions use that chemical energy to produce stable, high-energy sugars from carbon dioxide and water.
Alternative Biochemical Pathways • C4 Pathway – Plants in hot, dry climates. Try to prevent water loss. Water loss occurs through the stomata. (Passageway for O2 & CO2 entering and leaving the plant.) • CAM Pathway – open stomata only at night. • C3 , C4 & CAM pathway plants also differ by the initial product of carbon fixation.
Factors affecting the Rate of Photosynthesis: • Light Intensity • Amount of CO2 • Temperature