A Quantitative Study on Software Optimizations for Cache Performance
170 likes | 307 Vues
This study investigates software optimizations to improve cache performance given the performance gap between processors and memory. By applying compile-time techniques, we aim to reduce cache misses without hardware changes. Key analysis focuses on block size, associativity, cache size, and replacement methods, with methods including array merges, loop interchange, loop fusion, and blocking techniques. The research evaluates these optimizations through specific code examples, assessing their effectiveness in enhancing memory hierarchy efficiency and overall performance.

A Quantitative Study on Software Optimizations for Cache Performance
E N D
Presentation Transcript
A Quantitative Study on Software Optimizations for Cache Performance ECE 510 Yingfu Jiang Dec. 9, 2005
Motive • The increasing performance gap between processors and main memory has inspired compiler writers to scrutinize the memory hierarchy to see if compile time optimizations can improve performance. • Software optimizations are good ways to reduce cache misses without changes or additions to the hardware. • Instruction misses vs. data misses.
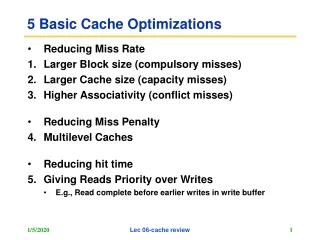
Analysis • Block size • Associativity • Cache size • Replacement method • Array size
Techniques The evaluation will be performed by attempting to reduce cache misses using following techniques • Array merges • Loop interchange • Loop fusion • Blocking
#define SIZE Nint main(){ int a[SIZE][SIZE], i, j; for (j = 0; j < SIZE; j++) { for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { a[i][j] = 2 * a[i][j]; } } return 0;} #define SIZE Nint main(){ int a[SIZE][SIZE], i, j; for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { for (j = 0; j < SIZE; j++) { a[i][j] = 2 * a[i][j]; } } return 0;} Loop interchange
#define SIZE Nint main(){ int a[SIZE][SIZE], b[SIZE][SIZE], c[SIZE][SIZE], d[SIZE][SIZE], i, j; for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { for (j = 0; j < SIZE; j++) { a[i][j] = b[i][j] * c[i][j]; } } for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { for (j = 0; j < SIZE; j++) { d[i][j] = a[i][j] + c[i][j]; } } return 0;} #define SIZE Nint main(){ int a[SIZE][SIZE], b[SIZE][SIZE], c[SIZE][SIZE], d[SIZE][SIZE], i, j; for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { for (j = 0; j < SIZE; j++) { a[i][j] = b[i][j] * c[i][j]; d[i][j] = a[i][j] + c[i][j]; } } return 0;} Loop fusion
#define SIZE Nint main(){ int a[SIZE][SIZE], b[SIZE][SIZE], c[SIZE][SIZE], d[SIZE][SIZE], i, j; for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { for (j = 0; j < SIZE; j++) { a[i][j] = b[i][j] * c[i][j]; } } for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { for (j = 0; j < SIZE; j++) { d[i][j] = a[i][j] + c[i][j]; } } return 0;} #define SIZE Nint main(){ struct merge { int a; int b; int c; int d; }; struct merge m[SIZE][SIZE]; int i, j; for (j = 0; j < SIZE; j++) { for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { m[i][j].a = m[i][j].b*m[i][j].c; } } for (j = 0; j < SIZE; j++) { for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { m[i][j].d = m[i][j].a+m[i][j].c; } } return 0;} Array merges
#define SIZE Nint main(){ int a[SIZE][SIZE], b[SIZE][SIZE], c[SIZE][SIZE], d[SIZE][SIZE], i, j; for (j = 0; j < SIZE; j++) { for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { a[i][j] = b[i][j]*c[i][j]; } } for (j = 0; j < SIZE; j++) { for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { d[i][j] = a[i][j]+c[i][j]; } } return 0;} #define SIZE Nint main(){ struct merge { int a; int b; int c; int d; }; struct merge m[SIZE][SIZE]; int i, j; for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { for (j = 0; j < SIZE; j++) { m[i][j].a = m[i][j].b*m[i][j].c; m[i][j].d = m[i][j].a+m[i][j].c; } } return 0;} Array merges, Loop interchange, Loop fusion
#define SIZE Nint main(){ int a[SIZE][SIZE], b[SIZE][SIZE], c[SIZE][SIZE], i, j, k, r; for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { for (j = 0; j < SIZE; j++) { r = 0; for (k=0; k< SIZE; k++) { r=r+b[i][k]*c[k][j]; } a[i][j]=r; } } return 0; } #define SIZE N int main() { int a[SIZE][SIZE], b[SIZE][SIZE], c[SIZE][SIZE], i, j, k, r, jj, kk, B, mm, nn; B=SIZE/10; for (jj = 0; jj < SIZE; jj=jj+B) for (kk = 0; kk < SIZE; kk=kk+B) for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { mm=jj+B-1; if (mm > SIZE) mm = SIZE; for (j = jj; j < mm; j++) { r = 0; nn=kk+B-1; if (nn > SIZE) nn=SIZE; for (k=kk; k<nn; k++) { r=r+b[i][k]*c[k][j]; } a[i][j]=a[i][j]+r; } } return 0; } Blocking
Future Work • L2 Cache… • Cache configuration (tradeoffs) • Benchmarks • Other optimizations