The Classical Hall Effect
120 likes | 566 Vues
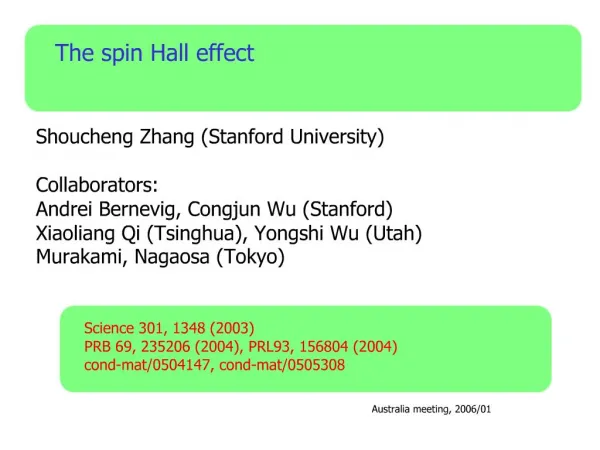
The Classical Hall Effect. Tim Morgan. A Simple Example. Current in Conductor or Semi-conductor Free Charge Carriers: Electrons and Holes Apply a magnetic field perpendicular to current Electrons and holes create potential Equilibrium of forces restores flow of current. The Hall Bar.

The Classical Hall Effect
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Classical Hall Effect Tim Morgan
A Simple Example • Current in Conductor or Semi-conductor • Free Charge Carriers: Electrons and Holes • Apply a magnetic field perpendicular to current • Electrons and holes create potential • Equilibrium of forces restores flow of current Tim Morgan | 5.31.05 | UA | Hall Effect
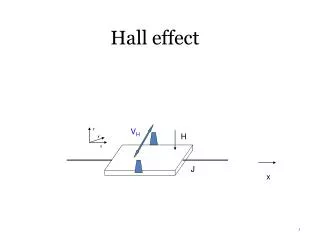
The Hall Bar Tim Morgan | 5.31.05 | UA | Hall Effect
The Hall Effect at Work • Magnetometers • Change in magnetic field produces change in current and hall voltage • High sensitivity in ammeters and voltmeters will detect smallest changes • Material Characterization • Determine properties of material that will give us high magnetic sensitivity • Need high mobility and high velocity material Tim Morgan | 5.31.05 | UA | Hall Effect
Measurement Techniques • Contacts • Material, shape and method affect results • Four Point Probe (fpp) method • One pair voltage, other pair current • Probe wander error • Measures resitivity • MMR machine • Measures Hall effects Tim Morgan | 5.31.05 | UA | Hall Effect
Sample Geometry • Hall-bar not often used • van der Pauw Structures • Random shape with uniform thickness • Common shapes: • Square • Greek Cross • Circle – two types • Clover-leaf • Fabrication and contact considerations Tim Morgan | 5.31.05 | UA | Hall Effect
Important Characterization Terms • VH – Hall Voltage • RH – Hall Coefficient • r – Hall Factor • μH – Hall mobility • ρ – Resistivity • n – electron density • p – hole density • τ – relaxation time Tim Morgan | 5.31.05 | UA | Hall Effect
Relationships & Equations • Hall Coefficient: • RH = r/(e*n) • Carrier Velocity: • v = μ * E • Mobility (Hall): • μH = |RH*σ| • Carrier Density: • nH = (jx*B)/(e*Ey) Tim Morgan | 5.31.05 | UA | Hall Effect
Sources of Error • Sample Preparation • Contacts • Sample Shape • Improper dimension ratios • Secondary band conduction • Sample Impurities Tim Morgan | 5.31.05 | UA | Hall Effect
Questions • Concerning the content of the presentation • Any corrections? • Additional information or depth? • Concerning research project • What more do I need to know? Tim Morgan | 5.31.05 | UA | Hall Effect
References • P. Blood, J. W. Orton. The Electrical Characterization of Semiconductors: majority Carriers and Electron States. Philips Research Laboratories. London. 1992. • D. C. Look. Electrical Characterization of GaAs Materials and Devices. Wright State University. Chichester. 1989. Tim Morgan | 5.31.05 | UA | Hall Effect