Neurulation
750 likes | 2.58k Vues
Neurulation. By Brett & Joshua. These slides will be uploaded after tonights session. Please see presenter notes under the slides for a description of the pictures. Objectives. Describe the formation of the morula and blastocyst and the process of blastocyst implantation

Neurulation
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Neurulation • By Brett & Joshua
These slides will be uploaded after tonights session. • Please see presenter notes under the slides for a description of the pictures.
Objectives Describe the formation of the morula and blastocyst and the process of blastocyst implantation Describe the process and resultant effect of gastrulation Describe the main derivatives of the 3 core embryonic tissues (endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm) Describe the longitudinal and lateral folding of the embryo and describe the cavities, structures and regions that this create Describe the process and result of ‘reversal’ during folding Describe the process and result of neurulation (neural tube formation), how the notochord is involved and describe the range of defects that can occur Describe the origin of neural crest cells, their migration and the tissues that they form/contribute toward Explain the basic structure, content and arrangement of the pharyngeal arches and the outline the regions that they become (more of this in later blocks) Review the formation of the gut tube and the defects that can occur R G Tunstall 2013
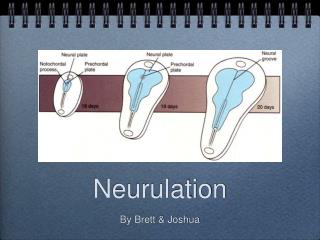
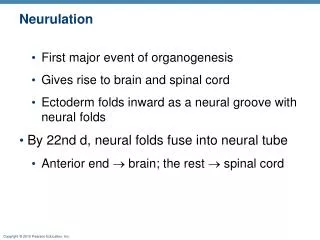
What is neurulation? • The formation of the neural tube, which later develops into the brain, spinal cord and retina
What are the three germ layers? • Ectoderm • Mesoderm • Endoderm
From which germ layer does the neural tube derive? • Ectoderm What else is derived from ectoderm? • Skin
1 4 2 5 3
Neural Crest Cell Migration Cells from neural crest migrate & form many important structures ~ Day 19 Crest cells are involved in: Dorsal root ganglia Adrenal medulla Melanocytes Meninges (Arachnoid & pia) Autonomic nerve ganglia GI tract ganglia (Parasympathetic) Septation of heart Skull & face connective tissues ~ Day 21 DAMMAGeSS Crest cells spread throughout body Re-differentiate into other cell types Defective neural crest cell migration – malformed face, nervous system absences, cardiac/gut defects R G Tunstall 2013
Tube Closure • Tube has two openings - at cranial end and at caudal end • What are these called? • Neuropores • When does each close? • Cranial day 25 • Caudal day 27
Neural Tube Defects Prevention?
What is neurulation? • The formation of the neural tube, which later develops into the brain, spinal cord and retina
What embryological structure sends signals to initiate neurulation? • Notochord
What is the region above the notochord called? • Neural plate
The neural plate involutes to form the...? • Neural groove
What is the name of the cells indicated by the black dots? • Neural crest cells
Name THREE things the neural crest cells migrate and redifferentiate to become. [3] Crest cells are involved in: Dorsal root ganglia Adrenal medulla Melanocytes Meninges (Arachnoid & pia) Autonomic nerve ganglia GI tract ganglia (Parasympathetic) Septation of heart Skull & face connective tissues DAMMAGeSS
The neural tube longitudinally but is open at either end. What are these endings called? • Neuropores
What is this called? • Spina bifida occulta
What other feature might someone with spina bifida occulta have? • Tuft of hair over region
What is this called? • Meningiocoele
What is this called? • Myelomeningiocoele
How can spina bifida be prevented? • Folic acid supplements during pregnancy