Indicators
130 likes | 292 Vues
Indicators. Definition: A quantitative or qualitative measure of programmatic performance that is used to demonstrate change and which details the extent to which programme results are being or have been achieved. Brief Presentation on Indicators. Lisa Bohmer, MPH Fistual M&E Meeting

Indicators
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Indicators Definition: • A quantitative or qualitative measure of programmatic performance that is used to demonstrate change and which details the extent to which programme results are being or have been achieved
Brief Presentation on Indicators Lisa Bohmer, MPH Fistual M&E Meeting Niamey, April 21-22, 2005 Sources: Programme Manager’s Planning Monitoring and Evaluation Toolkit. Tool Number 6: Programme Indicators Part I UNFPA and Guide for Designing Results-Oriented Projects and Writing Successful Proposals IPPF WHR
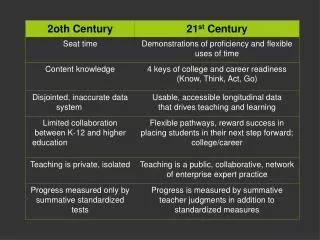
Common ways of expressing indicators: Quantitative Quantitative indicators are statistical measures • Number • Percent • Rate (ex. Birth rate – Births per 1,000 pop) • Ratio (ex sex ratio – Number of males per number of females)
Common ways of expressing indicators: Qualitative Qualitative indicators imply qualitative assessments • Compliance with • Quality of • Extent of • Level of Note: it is possible to express quantitatively via a scoring system (e.g. scoring system could be developed to track improvements in quality
Expression of indicators • While indicators measure change, they should not indicate the direction of the change. For example, • “increase in age at pregnancy” should be • “age at first intercourse among females aged 10-19” • If two or more measures are taken over time, the data will indicate if this age increased, decreased or stayed the same.
Expression of indicators • If indicators are written as percentages, both the numerator and denominator should be specified • For example: Percentage of religious leaders participating in the training session who know the three delays • Rather than: Percentage of religious leaders who know the three delays
Two basic types of indicators: Results and Process Results Indicators: • provide information about whether an expected change occurred at either program or population level • Measure changes that your program’s activities are seeking to produce in your focus population
Two basic types of indicators: Results and Process Process Indicators: • Provide evidence of whether the project is moving in the right direction to achieve an objective • Provide information about implementation of activities (what and how many conducted etc.)
Example results indicators: -Proportion deliveries assisted by SBA -% community members that have knowledge of fistula and prevention -% of treated women that receive post-operative counseling Example process indicators: -# of providers trained -# of women treated -# of treatment facilities for a specific country -# of organizations involved in fistula work Two basic types of indicators: Results and Process
Guidelines for Selecting Indicators: Indicators should be: • Direct: closely measure intended change • Objective: unambiguous about what is being measured and which data to be collected; clear operational definition • Practical: reasonable in terms of data collection cost, frequency and timeliness for decision-making • Adequate: the MINIMUM # of indicators necessary to ensure that progress towards the output/objective is sufficiently captured
Evolution of Indicators • Indicators evolve with a program as data becomes available • They need to be re-assessed and modified as appropriate
Good practices in identifying indicators • Ownership – involve key stakeholders • Include implications for data collection (including budget) in program design • Baseline information – obtain whenever possible • Use existing data sources and reporting systems where possible (or rapid assessment methodologies as a cost-effective alternative) • Establish partnerships with others to reduce cost of data collection • Plan for development of information management systems