Understanding Work and Energy: Key Concepts in Physics
150 likes | 277 Vues
Work and energy are fundamental concepts in physics, describing how forces cause movement and the capacity to perform work. Work occurs when a force causes an object to move, calculated as Work = Force x Distance, measured in Joules (J). Energy exists in various forms, including kinetic energy (KE) and potential energy (PE). Kinetic energy relates to an object's motion, while potential energy is linked to its position or shape. This guide explores the different forms of energy, including thermal, chemical, electrical, sound, light, and nuclear energy, illustrating the principles that govern them.

Understanding Work and Energy: Key Concepts in Physics
E N D
Presentation Transcript
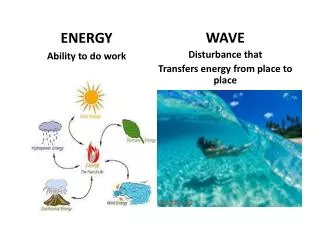
energy Ability to do work ___________________ ___________________________ occurs when a force causes an object to move in the direction of the force _______________________________ work
force distance Work = ____________ x _________ When work is done _______________ is given by 1 object to another energy
Joule (J) Work & energy units _________________ 1 J = amount of energy to lift an apple 1 m Average serve of tennis ball = 75 J of KE Fastball pitch = 120J of KE Football pass = 150J of KE Energy of motion ___________________ kinetic energy
KE = mv2 2 _______________ has a greater effect on kinetic energy than _____________ KE of a snail (mass 5g) traveling at 0.014 m/s0.00000048J KE of an 18-wheel truck traveling at 26.69 m/s 2,200,000 J speed mass
Energy of an object due to its position or shape ______________________________ _________________potential energy (GPE) is work done on an object when opposing the force of gravity; work done on an object to lift it to a given height potential energy gravitational
GPE depends on ________________ & ____________ GPE = weight x height Units (N x m ) = ___________ weight height Joule (J)
PE of a stretched bungee or a stretched rubber band _____________________ elastic potential energy
Total energy of motion and position ____________________________ Can be ____, ____, or _______ ME = PE + KE Mechanical Energy PE KE both
Forms of energy ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ _________________________ _________________________ thermal chemical electrical sound light nuclear
Thermal Total energy of particles in an object More energy if ________________________ _________________________ moving fast more particles
Chemical Work done to form compound is stored in chemical bonds between _________ Form of __________________energy __________ consists of chemical compounds atoms potential food
Electrical Energy of _________________________ Electrical energy of moving electrons is used to__________________________ Form of _____________________energy moving electrons do work kinetic
Sound Cause by an object’s _________________ which transmit ________________ from ______________ to ___________ Form of ___________ & _________ energy vibrations energy particle particle kinetic potential
Light Caused by the _____________ of electrically charged particles which transmit _____________________ vibrations energy
Nuclear Energy associated with changes in the _______ Produced when ____ nuclei join (ex: hydrogen in sun forms heliumcan only occur at 100,000,000 oC) Or When ____ nucleus splits (ex: PE stored in uranium) nucleus 2 1




















![[READ DOWNLOAD] AMA Guides to the Evaluation of Work Ability and Return to Work](https://cdn7.slideserve.com/12532724/slide1-dt.jpg)