Connective Tissue Types: Cartilage Overview by Dr. Jack L. Haar
210 likes | 336 Vues
Explore the structure and functions of different types of cartilage, its histological components, growth processes, and distribution. Learn how cartilage supports tissues, muscles, and acts as a transition form in the body.

Connective Tissue Types: Cartilage Overview by Dr. Jack L. Haar
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Connective Tissue TypesCartilage Dr. Jack L. Haar Department of Anatomy Sanger Hall 9-064
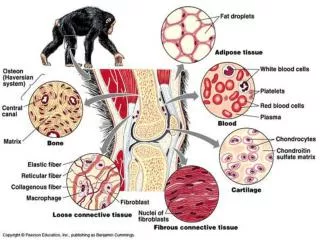
Cartilage • General considerations • Light, flexible, much intercellular substance • Forms quickly • Nutrients supplied by diffusion, no blood vessels
Histological components • Cells • Chondroblasts • Come from mesenchymal cells or multipotential C.T. cells • Differentiate to produce cartilage matrix
Chondrocyte (mature cartilage cell)Located in lacunaeGolgi, rER , fat droplet possible
Intercellular matrixFiber type depends on type of cartilageGround substance, mainly chondroitin sulfateTerritorial and interterritorial matrix
Perichondrium • Fibrous layer of dense C.T. • Chondrogenic layer of chondroblasts
Growth of cartilage • Appositional • Interstitial
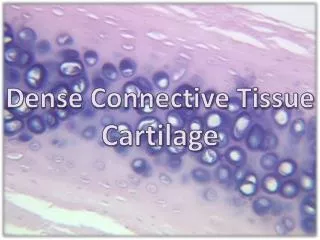
Types of cartilageHyaline Cartilage – type II collagen Distribution: nose larynx, strachea, bronchi
Elastic Cartilage • Abundant elastic fiber • Branching network • Limited ground substance
Distribution • External ear, epiglottis, part of the larynx
Fibrocartilage • “Never occurs alone but blends insensibly with neighboring hyaline cartilage, fibrous tissue or bone” • Fiber component • Bundles of collagen type I fibers fill matrix • Chondrocytes • May appear in parallel rows or randomly distributed • Occur in lacunae • Minimal ground substance • Function: strength and transition
Function:Provides stiffness and great tensile strength at tendon insertions
Function: A transition form from dense FECT and cartilage, provides shock absorption
DistributionIntervertebral disc Annulus fibrosus Nucleus pulposus
Regressive changes in cartilagea.Chondrocytes greatly hypertrophy, produce alkaline phosphatase, a calcifiable matrix; b. Calcium phosphate is deposited in matrix; does not allow diffusion of nutrients c. Chondrocytes die leaving behind the calcified matrix
Occurrencea. In some cartilage as it ages b. As early stage of bone production
http://www.path.uiowa.edu/virtualslidebox/ Table of Contents Supporting tissue and muscle Hyaline cartilage #5 Elastic cartilage #7http://java.vcu.edu/som-histology/