Understanding Magnetic Forces and the Hall Effect in Charged Particle Motion
170 likes | 326 Vues
This comprehensive overview explores the principles of magnetic forces acting on moving charges, including the Hall Effect, which describes charge buildup in conducting strips under crossed electric and magnetic fields. We discuss how the Hall voltage can be utilized to determine carrier density and characteristics. Additionally, we delve into synchrotron motion, magnetic torque on current loops, and the potential energy of magnetic dipoles, providing relevant equations and problem examples to illuminate these concepts in electromagnetic theory.

Understanding Magnetic Forces and the Hall Effect in Charged Particle Motion
E N D
Presentation Transcript
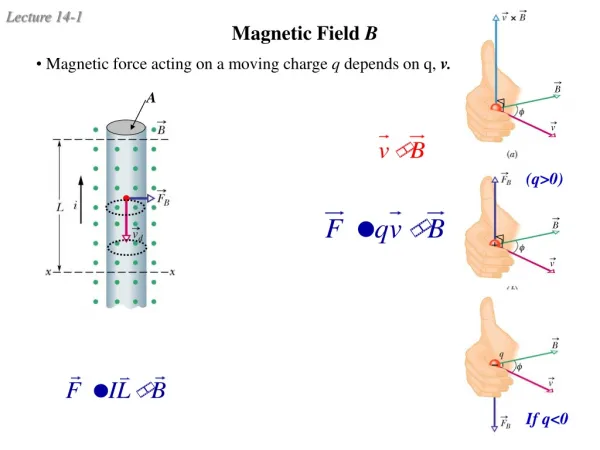
A If q<0 Magnetic Field B • Magnetic force acting on a moving charge q depends on q, v. (q>0)
EH EH Hall Effect • A conducting strip in crossed E and B fields • Applied E along the strip leads to a charge buildup on the sides of the strip and thus an electric field EH develops to both applied E and B. • Determines the sign and number of carriers. • Measures B.
Hall voltage EH EH for a given current I and n Carrier Sign and Density from Hall Effect Sign and density of charge carrier is determined at equilibrium and
increases as v does Cyclotron • "Magnetic Resonance Accelerator" • "Dees" in constant magnetic field B • Alternating voltage V is applied between the Dees at the orbital frequency f: • Particle will acquire an additional kinetic energy T = qV each time it crosses the gap (ie twice per revolution.. E=0 in Dees!). problems synchrotron
Synchrotron R is the same since B increases as v does
Also non-uniform B magnetic bottle Van Allen belts More complicated situations? v is not perpendicular to B helical motion (spiral)
Polar Light High energy particles leaked out of the belt and interact with the earth atmosphere.
Warm-up An electron (charge -e) comes horizontally into a region of perpendicularly crossed, uniform E and B fields as shown. In this region, it deflects upward as shown. What can you do to change the path so it remains horizontal through the region? Increase E Increase B Turn B off Turn E off Nothing http://canu.ucalgary.ca/map/content/force/elcrmagn/simulate/magnetic/applet.html http://canu.ucalgary.ca/map/content/force/elcrmagn/simulate/exb_thomson/applet.html
closed loop Magnetic Force on a Current Loop Force on closedloop current in uniform B? • Force on top path cancels force on bottom path (F = IBL) • Force on right path cancels force on left path. (F = IBL) Uniform B exerts no net force on closed current loop.
Definition of torque: abut a chosen point Magnetic Torque on a Current Loop • If B field is to plane of loop, the net torque on loop is also 0. B • If B is not , there is net torque.
area of loop Calculation of Torque • Suppose the coil has width b (the side we see) and length a (into the screen). The torque about the center is given by: • Define magnetic dipole moment by where n is normal to the loop with RHR along I.
A thin non-conducting disk of mass m and uniform surface charge density rotates with angular velocity as shown. What is the magnetic moment? mag. moment of the ring shown: dI Example of Magnetic Moment Calculation
Work must be done to change the orientation of a dipole (current loop) in the presence of a magnetic field. Potential Energy of Dipole B x • Define a potential energy U (with zero at position of max torque) corresponding to this work. . q Þ Therefore, Þ Þ
m x B B B t= mB m m x x X positive work Potential Energy of Dipole Illustrated t= 0 U = -mB t= 0 U =mB U = 0 max torque min. energy max. energy negative work (by YOU)
PHYS241 - Quiz A An electron (charge e) comes horizontally into a region of perpendicularly crossed, uniform E and B fields as shown. In this region, it is deflected upward as shown. What can you do to change the path so it deflects downward instead through the region? a. Increase E b. Turn B off c. Decrease E d. Slow down the electron e. None of the above
PHYS241 - Quiz B A proton (charge +e) comes horizontally into a region of perpendicularly crossed, uniform E and B fields as shown. In this region, it goes straight without deflection. What can you do to change the path so it deflects upward through the region? a. Increase E b. Increase B c. Turn B off d. Slow down the proton e. None of the above
PHYS241 - Quiz C A proton (charge +e) comes horizontally into a region of perpendicularly crossed, uniform E and B fields as shown. In this region, it deflects downward as shown. What can you do to change the path so it remains horizontal through the region? a. Increase E b. Turn B off c. Turn E off d. Slow down the electron e. Increase B