Observation vs. Inference
540 likes | 1.4k Vues
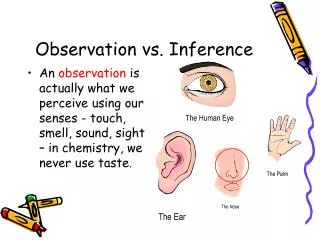
On the back of page 10 in your science notebook, write a paragraph (3 – 5 sentences) about what you think is going on in this picture. . Observation vs. Inference. The scientific method. Observations. An observation is the gathering information using your 5 senses: Sight Smell Hearing

Observation vs. Inference
E N D
Presentation Transcript
On the back of page 10 in your science notebook, write a paragraph (3 – 5 sentences) about what you think is going on in this picture.
Observation vs. Inference The scientific method
Observations • An observation is the gathering information using your 5 senses: • Sight • Smell • Hearing • Taste • Touch • Two types of observations! • Qualitative • Quantitative
Qualitative Qualitative observations DESCRIBE what we are looking at! Qualitative means quality! These types of adjectives are DESCRIPTIVE words. Example: The tractor is yellow. Example: The bird is blue.
Quantitative Quantitative observations are words used for MEASURING! Quantitative means quantity or how many! These observations are numerical and use NUMBERS to describe something. Example: The tractor has 4 tires. Example: The bird has 2 feet.
Which is better? • In science, both types of observations are powerful and useful! • However: • Qualitative observations can be better compared to other things • Quantitative observations assist with data collection and graphing. • Example • The bread rose. • The bread rose 4 inches.
Inferences Inferences explain HOW you know your observation. These are often times based on previous experiences. Example: Observation – The grass outside is wet. Inferences – It rained. The sprinkler was on. There is dew on the grass. A dog peed! (Ew!) All of these statements could be the explanation as to HOW the grass got wet.
Example • Observation: The school fire alarm is going off. • Qualitative: The school fire alarm is going off and it is loud. • Quantitative: The school fire alarm has been going off for 5 minutes. • Possible Inferences: • The school is on fire. • We are having a fire drill. • A student pulled the fire alarm.
Group example Observation: A student is sitting in the main office. Qualitative: Quantitative: Possible Inferences: