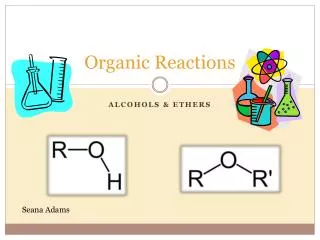
Understanding Organic Reactions: Addition, Elimination, Substitution, and Oxidation
180 likes | 300 Vues
Dive into the essential types of organic reactions: addition, elimination, and substitution reactions, with a keen focus on oxidation processes. Discover how alkanes undergo halogenation and how aromatic compounds react through various substitutions, including nitration and alkylation. Learn about oxidation reactions involving alcohols and aldehydes, and explore condensation and hydrolysis reactions in organic chemistry. This resource provides illustrations, structural formulas, and practical exercises to reinforce your learning.

Understanding Organic Reactions: Addition, Elimination, Substitution, and Oxidation
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Organic Reactions - II Chapter 1
Four Types • Addition Reactions • Elimination Reactions • Substitution Reactions • Oxidation • AESO………………………
Substitution Reactions • An H atom or a functional group is replaced by a different atom or functional group | | — C — X + AY → — C — Y + AX | |
Substitution Reaction of Alkanes • Halogenation: Reaction with Halogen, X2 • Produces RX + HX; additional halides may be produced • heat or UV light and a catalyst is required
Practice it Now!! • Write the structural formula of the product(s) formed • when propane reacts with excess of bromine in the presence of UV light. • When cyclohexane reacts with bromine in the presence of UV light.
Substitution Reaction of Aromatic compounds • Reaction with Halogen, X2 : Halogenation forming Ø – X + HX (iron (III) bromide, FeBr3, catalyst) • Ø – represents the aryl group • Reaction with Nitric acid, HNO3 : Nitration forming Ø – NO2 (nitro) + HOH • Reaction with Alkyl halide, RX : Alkylation forming Ø – R + HX
Aromatic Substitution Reactions • Halogenation: substitution of H with a halogen (X = Cl, Br, I, F) • Nitration: substitution of H with a –NO2 (nitro group)
Aromatic Substitution Reactions • Alkylation: substitution of H with an Alkyl group (C-chain) Let’s Practice it Now!! Complete Q# 4 (a) and (b) on page 30 of your textbook.
Oxidation Reaction • A reaction in which a carbon atom forms more bonds to oxygen, O, or less bonds to hydrogen, H. • An oxidizing agent (O) removes two H atoms from a carbon (one from an –OH group) resulting in the formation of double C=O bonds. • Generally, more carbon-oxygen bonds are formed during an oxidation. • Alcohols and aldehydes show this type of reaction.
Oxidation Reactions • Alcohols undergo oxidation to form aldehydes and ketones • oxidizing agent, such as H2O2, Cr2O7-2, KMnO4 in H2SO4 are required
Oxidation Reactions • Aldehydes undergo oxidation to form carboxylic acids (RCOOH) and HOH • oxidizing agent, such as H2O2, Cr2O7-2, KMnO4 in H2SO4 are required • Ketones are not oxidized under these conditions as they lack the critical H for the elimination to occur
Practice it Now . Draw structural diagrams to illustrate the following reactions. • oxidation of 1- propanol • Oxidation of 2- butanol • Oxidation of 2-butanal
Special Reactions • Condensation Reaction • Hydrolysis Reactions • Polymerization Reactions • Condensation reaction: • Two molecules combine to form a single organic molecule. • A small molecule, usually water, is also produced. • Is considered as an elimination reaction.
Condensation Reaction- also called as dehydration synthesis | | | | — C — OH + HO — C — → — C — O — C — + HOH | | | | | | | | | — C — OH + H2N — C — → — C — N — C — + HOH | | | • Alcohols react with other alcohols to form ether + HOH • sulphuric acid, H2SO4, is used as a catalyst • Can be considered as an elimination reaction
Condensation Reaction- also called as dehydration synthesis • Carboxylic Acids react with alcohols to form ester (R-COO-R ) and water • Reaction is called Esterification • sulphuric acid, H2SO4, is required as catalyst • Is biologically very significant
Condensation Reaction- also called as dehydration synthesis • Carboxylic acids also react with amines (R-NH2) to form amide (R-CONH-R) and HOH • sulphuric acid, H2SO4, is used as a catalyst • Biologically very important
Hydrolysis Reactions • Water is added to a bond to split a large organic molecule apart. • This reaction is the reverse of a condensation reaction • Biologically significant - digestion
Hydrolysis Reactions- Saponification • Esters react with NaOH to form sodium salt of a carboxylic acid (Na+R-COO- )and an alcohol (R-OH) • Used for making soap