Confidentiality using Conventional Encryption
40 likes | 167 Vues
Chapter 5 explores the vulnerabilities associated with conventional encryption, highlighting risks from in-house threats such as compromised workstations and routers, as well as external attacks like man-in-the-middle and DNS spoofing. It discusses various encryption points, focusing on link encryption capabilities, user authentication, and the importance of end-to-end encryption for maintaining traffic confidentiality. The chapter also addresses defensive strategies, including traffic padding and packet tunneling to obscure communication patterns, thereby protecting sensitive information from traffic analysis.

Confidentiality using Conventional Encryption
E N D
Presentation Transcript
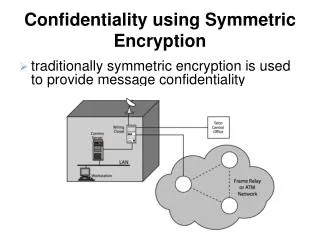
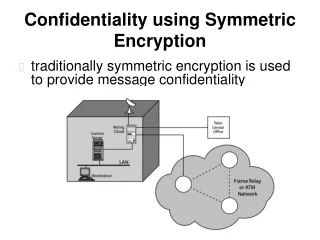
Vulnerability points • In-house • Corrupted workstation • Extra machine with sniffer • Wiring closet • Sneaky rewiring – for example to phone line • Corrupted server/router • Hacked – routed to man-in-the middle • Interception on external network • Wireless interception • Interception in external packet network • DNS attack • IP spoofing
Encryption points • Link encryption • IP and higher headers are encrypted – less traffic analysis • Requires trust in packet network • Many keys required • Host authentication only • End-to-end encryption • Link headers must be in clear • Packets show link headers • One key per user pair • User responsible and can decide not to encrypt • Can be either protocol (TCP layer) or application layer
Traffic Confidentiality • Defends against traffic analysis • Partner identity • How much communication • Message characteristics – length, response patterns • Relation with external events • Defenses • Link encryption hides users’ headers • Traffic padding (send useless random patterns) – used for end-to-end • Packet tunneling (real thing hidden within innocent-looking packet)