The Atomic Theory
230 likes | 260 Vues
This comprehensive guide explores the evolution of atomic theory from Dalton to modern concepts, including key discoveries by Thomson, Rutherford, and more. Learn about the fundamental principles of atoms, protons, neutrons, and electrons. Discover how atoms form elements and create new substances. Delve into the structure of the atom's nucleus and electron clouds. A journey through the history and advancements in understanding the smallest particles that make up all matter.

The Atomic Theory
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Atom • An atom is the smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still be the same substance.
Atomic Theory • The existence of atoms is not a new idea. Atomic theory has been around for more than 2,000 years. A theory is a unifying explanation for a broad range of hypotheses and observations that have been supported by testing.
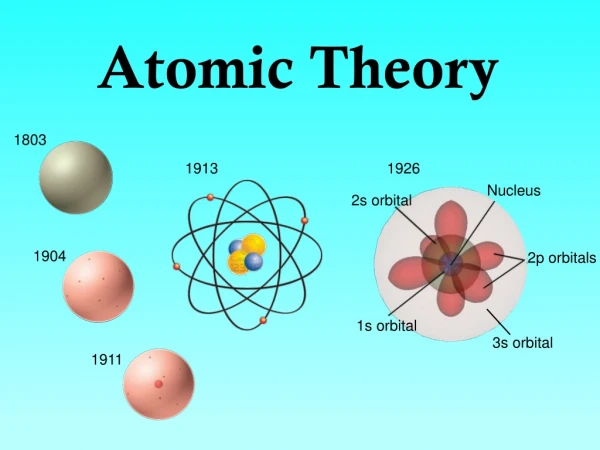
John Dalton • All substances are made of atoms. Atoms are small particles that cannot be created, divided, or destroyed. • Atoms of the same element are exactly alike, and atoms of different elements are different. • Atoms join with other atoms to make new substances.
J.J. Thomson • Thomson discovered that there are small particles inside the atom. Therefore, atoms can be divided into even smaller parts. • JJ Thomson is credited with discovering “ELECTRONS”
Ernest Rutherford • Rutherford proposed that in the center of the atom is a tiny, extremely dense, positively charged region called the “NUCLEUS”.
James Chadwick • The Neutron, one of the particles in the “Nucleus” of an Atom, is discovered by British physicist James Chadwick.
Niels Bohr • Bohr suggested that electrons traveled around the nucleus in definite paths. He proposed that no paths are located between the levels, but electrons can jump from a path in one level to a path in another level. (A very good example of this would be a “ladder”.)
The Modern Theory • According to the current theory, electrons do not travel in definite paths as Bohr suggested. In fact their paths can not be predicted. Regions inside the atom where electrons are likely to be found are called “ELECTRON CLOUDS”.
Do You Remember? http://go.hrw.com/activities/frameset.html?main=2333.html Questions 1-5