Chapter 3 India
250 likes | 401 Vues
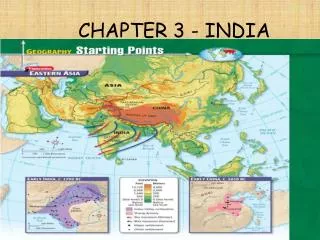
Chapter 3 India. Geography. Impact on society? Technology? Government?. Rivers Indus Ganges Brahmaputra Mountains Himalayan Hindu Kush Winds monsoons. Timeline of India. TIMELINE dates Indus Valley (Harriman) 2500-1500BC Aryan Civilization (Vedic) 1500-1000BC

Chapter 3 India
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Geography Impact on society? Technology? Government? • Rivers • Indus • Ganges • Brahmaputra • Mountains • Himalayan • Hindu Kush • Winds • monsoons
Timeline of India • TIMELINE dates • Indus Valley (Harriman) • 2500-1500BC • Aryan Civilization (Vedic) • 1500-1000BC • Mauryan Civilization • 320-185 BC • Gupta Civilization • 320AD -550AD
Basics on India • Government • Early – raja (local leader), later - kings • Religion • Hinduism, Buddhism • Writing • Sanskrit • Technology • Citadels (fortresses), inoculation • Society • Social hierarchy, caste system – rigid class system
Indus Valley Civilization • Cities: Harappa and MohenjoDaro • Well planned • Citadels: fortress • Large storehouses • Limited amount of evidence • Known: • traded with Mesopotamia
Aryan Civilization Came to India because of pasture/cattle Polytheistic – nature gods
Vedic Age (Aryan Civilization) Society: • Herders and farmers • caste system • Brahmins: teachers, scholars and priests • Kshatriyas: kings and warriors • Vaishyas: farmers and traders • Sûdras: artisans, labourers • Untouchables
Varna (Social Hierarchy) Brahmins Kshatriyas Vaishyas Shudras Pariahs [Harijan] Untouchables
Religion in Ancient India “There is only one God, but endless are his aspects and endless are his names”
Hinduism Monistic – unity of god and creation Brahma: The Creator Vishnu: The Preserver Shiva: The Destroyer Religious books called the Vedas Religious commentaries on Vedas called the Upanishads
Hinduism Shiva Vishnu
Society: Social Structure • Different castes are at different stages of nirvana • Because of this, lower castes were discriminated • What is the purpose of a caste system? • Why would people buy into this caste system?
Hindu terms Atman: soul Brahman: universal soul Nirvana (moksha): liberation/union Reincarnation: rebirth to achieve higher levels of existence Karma: good and bad incidents in life that allow your soul to advance Dharma: doingmoral duty in life to advance to the next life Maya: world we see is an illusion
Hinduism Reincarnation • People may be reincarnated at a higher or lower level of existence • the way one has lived in a previous life dictates into which caste you are born • depending on their karma • animals or a lower/higher caste as a human. • Death is not final for Hindus as they expect to be reborn many times.
Hinduism • Other Beliefs • Cows are sacred • Every living thing has a soul – • vegan or vegetarian • Ganges river is sacred • Freedom of belief • Yoga brings one closer to moksha
Buddhism • Reformer Siddhartha Gautama • TIMELINE – 563 BC • Four noble truths, Eight-fold path are way to Nirvana • Not based on caste system, based on ethics • Desire causes suffering • Buddhism gets reabsorbed back into Hinduism in India, become more popular in other parts of Asia
Asoka What are the major themes in Asoka’s edicts (what is the common message) How are his edicts similar to or different from Hammurabi? What would daily life look like in India as a result of these edicts
Women “Women must be honored and adorned by their fathers, brothers, husbands, and brothers-in-law.” “Where women are honored the gods rejoice. Her fathers protects her in childhood, her husband protects her in youth, her son protects her in old age – a woman does not deserve independence. “ “In regard to the highest dharma, husbands must strive to protect their wives “