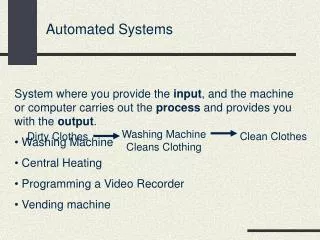
Automated Systems
100 likes | 334 Vues
Automated Systems. Lesson 4: Stationary v Mobile Robots. Lesson 4: Automated Systems. By the end of this lesson you will be able to:. Identify what the initials AGV stand for. Identify 2 guidance systems for AGVs.

Automated Systems
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Automated Systems Lesson 4: Stationary v Mobile Robots
Lesson 4: Automated Systems By the end of this lesson you will be able to: • Identify what the initials AGV stand for. • Identify 2 guidance systems for AGVs. • Suggest a suitable guidance system for an AGV working in a dirty environment. • Suggest a suitable guidance system for an AGV working in a clean environment. • Explain the term ROM software. • Give 2 advantages of using ROM softare. • Give 2 disadvantages of using ROM software. • Explain why real time processing is essential for AGVs. • Explain what it means to be an intelligent robot. • Explain the impact automation has had on the design of the workplace.
Lesson 3: Automated Systems Stationary v Mobile Robots • A stationary robot is fixed in one location in a workplace. • A mobile robot is a robot that can move around a workplace. • Mobile robots are some times called AGVs: Autonomous Guided Vehicles. • AGVs are often used in workplaces to fetch and carry parts from a warehouse to where they are needed
Lesson 4: Automated Systems OR OR Mobile Robot Guidance Systems • AGVs need to be have a guidance system to tell them how to get from A to B. • There are 2 types of guidance systems: • light guidance systems • magnetic guidance systems. • Which is best? • Which system is used depends on the: • how messy the workplace is and • how often the system might need to be changed.
Lesson 3: Automated Systems Control program instruction feedback Interface data Analogue signals vary in strength: eg temperature goes gradually up and down pressure gradually builds and fades. Sensor Digital signals are either 0 or 1: 00001110001100110 Interface An interface is needed between a sensor and the controlling computer. The interface is required because sensors are analogue yet the controlling computer understands digital data only. The interface converts the signals.
Lesson 3: Automated Systems 100oC 01100100 digital analogue 0 OFF digital analogue AD and DA Converters An AD converter is the interface that translatesanalogue data into digital data. AD Converter A DA converter is the interface that translatesdigital data into analogue data. DA Converter
Lesson 3: Automated Systems Questions Answer the following questions in your jotter. • Name the part of the automated system that control the action. • Why is a sensor needed? • List 3 types of sensors and explain what each could be used for. • Explain the term feedback. • Why is feedback necessary? • What happens as a result of feedback? • Explain why a interface is required. • Draw a diagram of where an interface will be positioned in system. • What is an AD converter? • What does a DA converter do and why?
Fun Things To Do Try programming the Picobot using it’s sensor. Try programming Lego Robot cars. Robots with a sense of touch http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2005/08/0817_050817_robotskin.html Beetles & Sensors http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2003/03/0314_030314_secretweapons3.html Robot Cars http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2005/10/1006_051006_robot_car_2.html Smart Cars http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2004/05/0521_040521_smartcars.html