Defining Accessibility
80 likes | 337 Vues
Defining Accessibility. Defining Accessibility. This PowerPoint will cover the following topics: Defining Accessibility Universal Design Principles of Accessible Design Examples of Accessibility Accommodations for Students Accommodation Process. What is Accessibility? .

Defining Accessibility
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Defining Accessibility • This PowerPoint will cover the following topics: • Defining Accessibility • Universal Design • Principles of Accessible Design • Examples of Accessibility • Accommodations for Students • Accommodation Process
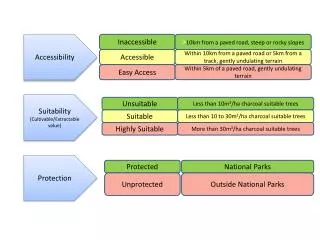
What is Accessibility? • Accessibility is a general term used to describe the degree to which a product (device, service, or environment) is accessible by as many people as possible. It is the ability to access the functionality, and benefit of a system or entity.
Seven Principles of Universal Design • Equitable use • Flexibility in use • Simple and intuitive • Perceptible information • Tolerance of error • Low physical effort • Size and space for approach and use “The Center for Universal Design (1997). The Principles of Universal Design, Version 2.0. Raleigh, NC: North Carolina State University”
Key Principles of Accessible Design • Provide alternative text • Provide document structure • Provide headers for data tables • Ensure users can complete and submit all forms • Ensure links make sense out of context – no “click here” links • Caption and/or provide transcripts for media • Design to standards From WebAIM – webaim.org
Examples of Accessibility for an Online Environment • Utilize a good heading structure and add alternative text for images for Microsoft Word documents • Create searchable PDFs • Utilize already designed templates and add alternative text for images for PowerPoint. Use Accessibility Checker in PowerPoint 2010. • Provide transcripts of audio clips • Provide closed captioning for video clips
Accommodations for Students • Ideally, all physical and digital environments would be universally accessible. • Universal design of content is ideal; universal design is the creation of documents and media in such a way that it is malleable for any circumstance and adapts to many situations and adaptive technology. • Accommodations are made for students to avoid any barriers to course content. • Accommodations are set so that all stakeholders (faculty and students) are aware of changes that may need to be made to the existing environment.
Accommodation Process • Students with disabilities register with Student Access Center • Students email professors a letter of accommodation • Students are encouraged to discuss accommodation needs with each professor • If professors have questions, there is a FAQ section under Faculty/Staff Information at www.ksu.edu/accesscenter or call the office at 785-532-6441