Quadratic Equations: Features and Forms
150 likes | 188 Vues
Discover the key features and different forms of quadratic equations, including roots, vertex, and max/min points. Learn how to convert between standard, vertex, and factored forms, solve equations, and find the axis of symmetry.

Quadratic Equations: Features and Forms
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Quadratic Equations • a quadratic equation is an equation of degree 2, meaning that the highest exponent of this function is 2.
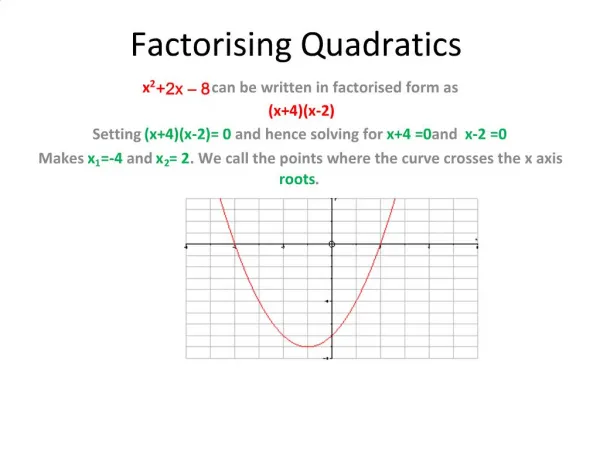
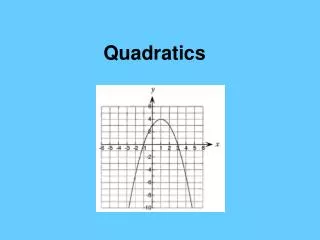
Key Features of a Quadratic Function • Roots (aka zeros, solutions, x-intercepts): Where the graph crosses the x-axis • Line of symmetry (aka mirror line): a line through the center of the graph that splits the graph into 2 reflected images
Key Features of a Quadratic Function • Vertex (aka the thing that no one wants to find algebraically): the point where the graph changes from increasing to decreasing or decreasing to increasing • Max/min (aka the vertex again): the highest (max) or lowest (min) point on the graph that is not infinity
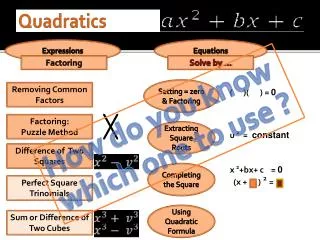
3 different forms of the quadratic equation • Standard form (the least useful) • Good for quadratic formula and not much else a Coefficient Shows whether opens up or down and vertical dilation (stretch) Y-intercept
3 different forms of the quadratic equation • Vertex form (the one you usually have to convert standard form to) • Best for graphing, tells you the vertex H and k will be numbers, the vertex will be the coordinate (h , k) Note the (–) in front of h Same a as standard form
3 different forms of the quadratic equation • Factored form (the one you have been doing since before algebra 1) • Best for solving quadratic equations which is really finding the x-intercepts of the graph Each () is set =0 and solved individually
Example • Convert to standard form, then factored form, then graph the function stating all the key features
Finding the axis of symmetry from standard form • Use the formula • How can we use this to find the vertex? • Can we use this to convert to vertex form?
Solving for Quadratic equationsaka: find the roots, solutions, zeros, x-intercepts • Multiple methods depending on which form of the equations you have to work with • The roots are the x-intercepts so they are located on the x-axis • X-axis is when y=0 so f(x)=0
Factored FormReview • Uses the zero product property • Set each binomial =0 • Solve each problem seperately
Quadratic Formula X coordinate of the vertex Also the axis of symmetry Horizontal distance from the vertex What does this part mean then? What does this mean on the graph?
Standard Form • Option one: convert to factored form and solve • Option two: Quadratic formula
Vertex Form • Solve like absolute value except… • Instead of making 2 equations, square root both sides • Is the answer + or -?