Populations in Ecosystems
280 likes | 314 Vues
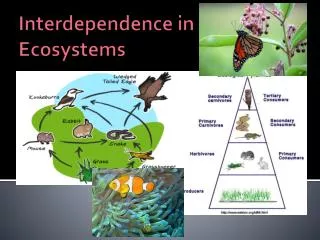
Populations in Ecosystems. Growth of Populations Long-Term Survival of Species Impact of Environmental Change Populations Respond to External Factors. A group of the same kind of organism that lives in the same place is called a …. POPULATION. CHARACTERISTICS OF POPULATIONS.

Populations in Ecosystems
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Populations in Ecosystems Growth of Populations Long-Term Survival of Species Impact of Environmental Change Populations Respond to External Factors
A group of the same kind of organism that lives in the same place is called a …. POPULATION
CHARACTERISTICS OF POPULATIONS Three important characteristics of a population are its: • Geographic distribution or range. • Population density – the number of individuals per unit area. • Growth rate
Density • Number of individuals per unit area • Varies depending on species and its ecosystem US Population Density 1990
POPULATION GROWTH Three factors can affect population size: • The number of births. • The number of deaths. • The number of individuals that enter or leave the population. A population can grow when its birthrate is greater than its death rate.
Exponential Growth • Under ideal conditions with unlimited resources, a population will grow exponentially. • Exponential growth occurs when the individuals in a population reproduce at a constant rate. • The population becomes LARGER and LARGER until it approaches an infinitely large size.
Turn to the person next to you and explain how the two graphs are similar OR different? Exponential Growth
Do populations really grow EXPONENTIALLY??Can populations continue to grow exponentially forever?What do you think?
Answer…..is….NO!! • As resources become limited (limiting resource), the growth of a population slows or stops. • The result looks more like the S-Shaped graph
Carrying Capacity • The environment can only HOLD or CARRY so many individuals • Largest number of individuals that a given environment can support = Carrying Capacity
What Limits Growth of a Population?LIMITING FACTORSFactor that causes population growth to DECREASE
Density Dependent Limiting Factors • Density-dependent factors operate only when a population is large and dense. • Examples: • competition • predation • parasitism • disease
Density Independent Limiting Factors • Density-independent affect all populations in a given area in similar ways, regardless of the population size. • Examples: • unusual weather like droughts • natural disasters like hurricanes, forest fire • seasonal cycles • certain human activities
What is Environmental Stability?How do ecosystems maintain stability despite constant limiting factors?
What is ecosystem stability? • The vast majority of natural ecosystems experience regular environmental change, or disturbances. • Most ecologists describe ecosystem stabilityas the ability of an ecosystem to maintain its structure and function over long periods of time despite disturbances.
How do Ecosystems maintain stability with all of these limiting factors?
Biodiversity • The sum total of the genetically based variety of all the organisms in the biosphere is called biodiversity. • Biodiversity is one of our greatest natural resources. Species of many kinds have provided us with many foods, industrial products, and medicines.
Environmental Adaptations • Populations have become adapted to live in specific conditions as a result of their environment. • For Example: • Desert cacti • Palm trees • Snow Owls
Threats to Biodiversity • Human activities can cause decreases in the amount of biodiversity by: • Habitat alteration -- Pollution • Improper hunting --Introduced species
Introduced Species • Throughout history humans have transported apparently harmless plants or animals which have become invasive in a new habitat. • Invasive species (also called exotic species or nonnative species) are those that rapidly increase their populations due to lack of natural predators and/or parasites thereby giving it an advantage over native species.
ASIAN CARP INVASION!!!!!!http://abcnews.go.com/Nightline/video/beware-asian-carp-invasion-12329740
How does environmental change affect ecosystem stability? • Changing environmental conditions can cause the decline of local biodiversity. • Ecosystems that are less stable may not be able to respond to a normal environmental disturbance.
How does natural environmental change affect ecosystem stability? • Fires, heavy storms, and natural climate change can cause major changes in local populations of plants and animals. • A decline in natural biodiversity can make an ecosystem less stable.
Something to think about for the future…. • How will the Earth’s increasing average temperatures affect ecosystem structures and functions? • Scientists are not yet sure how predicted changes in global climate within the next several decades will affect ecosystem stability worldwide.