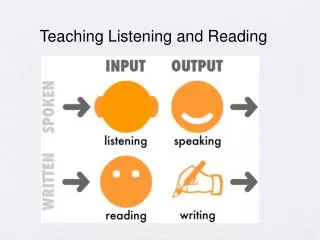
Teaching listening
290 likes | 1.12k Vues
Teaching listening. Teaching objectives. By the end of this unit, Ss will be able to: know the i mportance of listening know the difficulties Ss may encounter in listening Understand the nature and characteristics of the listening process know the principles for teaching listening

Teaching listening
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Teaching objectives By the end of this unit, Ss will be able to: • know the importance of listening • know the difficulties Ss may encounter in listening • Understand the nature and characteristics of the listening process • know the principles for teaching listening • know the stages in teaching listening • design common activities in teaching listening
Teaching content • Importance of listening • Difficulties Ss may encounter in listening • Nature and characteristics of the listening process • Principles for teaching listening • Stages in teaching listening • Common activities in teaching listening
Imitation vs. Communication “Language is learned through imitation” • Audio-Lingual Method • Grammar-Translation Method • Focus on Form • Repeat, repeat, repeat
Imitation vs. Communication “Language is learned through communication” • “Communicative Approaches” • Task-Basked Learning • Problem-Based Instruction • Learner-Based Instruction • Focus on Meaning
The importance of listening in daily communication • Rivers (1968) Listening:45%,Speaking: 30%Reading:16% Writing:9%
Brainstorming:Ask the students to list the difficulties they may encounter in listening.
Difficulties Ss may encounter 语言方面: 语音、语调、单词发音在句中的变化,如连读、同化、弱化、失去爆破, 还有重音、语调以及口语习惯表达方法、语法结构等。
Difficulties Ss may encounter 听的技能: 听文段大意和细节、确定中心思想、理解人物关系、推断作者意图、懂得因果关系、做出结论等等。
Difficulties Ss may encounter 文化背景知识: 如历史、地理、社会常识、思维方式、社交礼仪、价值观念、禁忌幽默、文化习俗等
Nature of the listening process Bottom-up: knowledge of sounds, vocabulary and grammar
Nature of the listening process Top-down : content schema: general knowledge/life experience textual schema: knowledge of situational routines topic, relationship between the speakers, the location
Charateristics of the listening process Spontaneity Context Visual clues Listener’s response Speaker’s adjustment
Principles for teaching listening • Expose students to different ways of processing information: bottom-up and top-down • Expose students to different types of listening: specific information, gist/global listening, inference
Consider text, difficulty, and authenticity • Teach listening strategies: predicting, inferring, monitoring, clarifying, responding, evaluating • Expose Ss to a variety of input
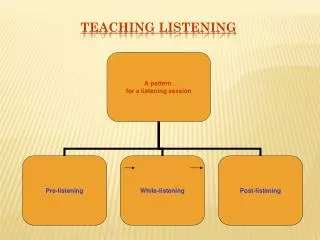
Stages in teaching listening • pre-listening • while-listening • post-listening
Stages in teaching listening • Pre-listening Purpose:Lead-in, activate schemata, arouse interest Activities:(p.145-148) Strategies: --previewing --predicting --setting the scene/context
Stages in teaching listening • While-listening Purpose:Checking comprehension Activities: (p.148-151) • Strategies: • --selective attention • --predicting • --note-taking • --elaboration/associate • --inferencing • --auditory representation
Stages in teaching listening • Post-listening Purpose:Expansion and development of listening tasks Activities: (p.152-154) • Strategies: --grouping --self-evaluation
Watch the video(优质课录像) • Task: Identify the activities in each of the three.
Assignment • Design a lesson plan of listening instruction and prepare to present it.