The Hydrosphere
110 likes | 739 Vues
The Hydrosphere. Earth and Space Grade 10 ST 2011. What is the Hydrosphere?. The Hydrosphere is the Earth’s outer layer of water- including water in its solid, liquid and gaseous forms Facts:

The Hydrosphere
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Hydrosphere Earth and Space Grade 10 ST 2011
What is the Hydrosphere? • The Hydrosphere is the Earth’s outer layer of water- including water in its solid, liquid and gaseous forms Facts: • Water is a precious resource. Fresh water in particular is extremely rare as it represents only 2.5 % of the water on Earth. • 79% of all fresh water is frozen in glaciers
Inland Waters • Inland waters are fresh water found on the continent. • They include • Rivers • lakes • groundwater.
Watersheds • A watershed is a region in which all the freshwater drains to the same large body of water. • The natural terrain (mountains, hills or high grounds) is what divides the different watersheds. • The natural slope of the land will cause the water to flow in the same direction
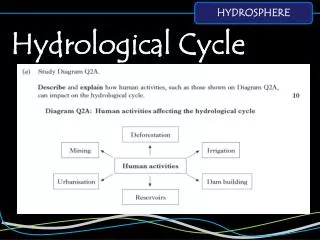
Watersheds Aspects that limit the flow of water 1) Topography: the shape, slope and terrain of the area. • Ex: steeply sloped land drains easier 2) Geology: the type, depth ands structure of the rock. • Ex: Water flows more easily through the holes of crushed rock than clay 3) Climate: rain or snowfall, winds and temperature. • Ex: water flows more quickly after a rainfall 4) Vegetation: density and diversity. • Ex: when it rains water movement is slowed by wooded areas. 5) Agricultural, industrial and urban development. • Ex: a dam can prevent water from flowing freely
Energy Resources from the Hydrosphere Water from rivers and waterfalls • The energy carried by moving water (hydraulic energy) can be transformed to electrical energy. In Quebec, this is the main method of supplying electricity. That is why we call it Hydro- Quebec.
Hydroelectric Power plants http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rnPEtwQtmGQ
Hydroelectric Power Plants How they work: • A dam is put across a river to hold back water • Water level rises • Dam gates open • Water rushes in • Water turns turbines • Turbines are connected to generators or alternators that convert the mechanical energy into electric current
Waves and Current Energy How are waves and ocean currents transformed into electrical energy? Buoys rise and fall with the current and waves. Mechanical energy from the rising and falling is converted to electrical energy Underwater turbines use ocean currents to turn and converts mechanical energy into electrical energy
Waves and Current Energy What is the ‘con’ to this type of energy resource?