GPIB CONTROLLERS
160 likes | 497 Vues
GPIB CONTROLLERS . Technical Seminar Presented By Ashutosh Pradhan EI200118107. Under the guidance of Miss. Suchilipi Nepak. INTRODUCTION. What is GPIB? GPIB is known as General Purpose Interface Bus.

GPIB CONTROLLERS
E N D
Presentation Transcript
GPIB CONTROLLERS Technical Seminar Presented By Ashutosh Pradhan EI200118107 Under the guidance of Miss. Suchilipi Nepak
INTRODUCTION • What is GPIB? • GPIB is known as General Purpose Interface Bus. • It is an industry standard published by IEEE. • It is adopted by IEEE-STD 488 in 1978.
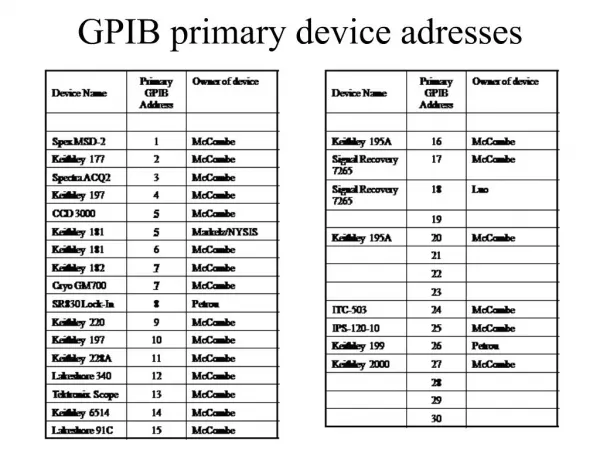
Physical Bus Structure • GPIB bus is composed of 16 signal lines. • 8 Bidirectional lines and NRFD,DAV,NDAC 3 handshake lines • Five lines are used to control bus’s operation. • ATN Attention • EOI End or Identify • IFC Interface clear • REN Remote enable • SRQ Service Request
The HS488 Protocol • Normal IEEE 488.1Handshake
Different Types Of Controllers • Plug-in controllers • External controllers • ASICs
Plug-in controllers • PCI • PXI • PCI Express
External controllers • Ethernet • USB • Fire Wire • Parallel Port • RS232 • RS485 • SCSI
Applications • Remote GPIB Control Using a GPIB-232CT-A
Remote modem Setup • Modem Connection • The GPIB-232CT-Functions in S-Mode • Establishing the Communication with Remote GPIB Controller. • Remote Interfacing With the GPIB-232CT-A. • Disconnecting from Remote GPIB Controllers. • General Programming Consideration.
Eight ways to increase the GPIB system performance • Bus-Mastering GPIB Controllers for PCI • 8-Mbyte/s-Compatible GPIB Controllers and Instruments . • GPIB Instrument Drivers Designed for High Performance. • Off-Loading Data Processing to the Host PC. • Using Multithreading in Software. • Using Native Instrument Data Formats • Using Modular Plug-in Instruments for Demanding Applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages • Easy to configure and use . • GPIB controller make suitable application for laptop computer or desktop applications. • Data transfer rate is more in comparison to other type of BUS. • we will communicated with limited no of device up to 14 GPIB devices. • The length of the cable for some GPIB Controllers has limited length. • Ethernet is not sufficient for all the uses as we have its higher version named WAGO Ethernet.
Conclusion • GPIB controllers are used in process industries and networking fields.It helps for quick data transfer and easy to handle. It has solutions for almost every desktop, laptop, and workstation. • It supports the software like LabVIEW. It has gained popularity in applications such as intercomputer communication and peripheral control. • These controllers have quickly build applications with configuration, troubleshooting and debugging tools.