POWER PLANT
290 likes | 678 Vues
POWER PLANT. Doç.Dr. BURHANETTİN ÇETİN. A power plant is the name given the 'factory' where electricity is generated. The major advance in power plant design was the development of the practical steam turbine by Parsons in 1884. Turbines rapidly superseded steam engines. .

POWER PLANT
E N D
Presentation Transcript
POWER PLANT Doç.Dr. BURHANETTİN ÇETİN
A power plant is the name given the 'factory' where electricity is generated. The major advance in power plant design was the development of the practical steam turbine by Parsons in 1884. Turbines rapidly superseded steam engines.
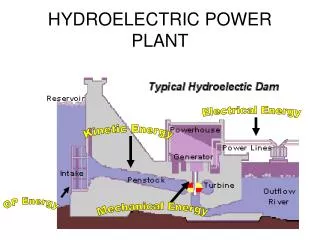
The power plant process occurs in two loops or circuits, the working fluid in both circuits is water. The primary circuit contains the following components: steam generating boiler, steam turbine, condenser, feedwater pump. The secondary circuit contains the condenser, cooling tower and recirculating pump.
Steam Generating Boiler: To produce steam, water must be boiled and latent heat of evaporation must be given. Latent heat is the heat or energy required to change the state of a fluid ( i.e. change the state of a liquid to gas) and it does no useful work.
When the steam is condensed in the Condenser, the latent heat is released and passed back into the cooling water in the secondary circuit. This latent heat represents the major loss from the cycle of about 35% to 40%.
The steam produced in the boiler is called ‘saturated steam’. Because it is contact with the liquid water in the boiler. To obtain high efficiency in a power plant, saturated-steam is further heated and produced 'superheated steam'.
Whenthe heated air (800 oC) leaves the boiler it would have lost most of its heat. This air also contains the combustion by-products (sulphur, carbon dioxide, etc.) and fly ash. These particles are removed by scrubbers. The air stream is then exited to the atmosphere up the chimney stack!
Steam Turbines The purpose of a steam turbine is to convert heat energy into mechanical energy.
Condenser Steam exhausted from the low pressure steam turbines enters the condenser. The condenser is essentially a heat-exchanger and operated at near vacuum conditions to enhance the pressure drop. So the efficiency improves.
Feedwater Pump The feedwater pump pumps the liquid water that was condensed in the condenser back into the boiler. The primary working fluid must be pumped at a slightly greater pressure than the boiler pressure to ensure that the fluid enters the boiler.
Cooling Towers. Cooling towers are very interesting and subtle machines. The shape of a cooling tower is called as 'venturi‘.
Electrical Generator. The rotating shaft of the steam turbine is coupled to the electrical generator. The speed at which the steam turbine is operated is very important, as this determined the electrical frequency.