Photosynthesis
190 likes | 318 Vues
This lesson explores the intricate process of photosynthesis, focusing on the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin Cycle. Students will learn about the reactants and products involved, as well as key components such as ATP, NADPH, chloroplast structure, and factors influencing photosynthesis. By the end, students will understand how plants convert light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose, and the significance of each reaction in the broader context of cellular energy production.

Photosynthesis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
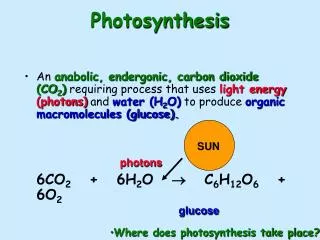
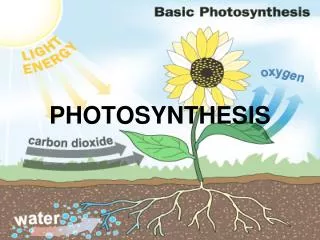
Photosynthesis • Objective • SWBAT Describe the process of photosynthesis • Bellringer • What are the products and reactants of photosynthesis?
Adenine Ribose 3 Phosphate groups • Cell Energy: • Cells usable source of energy is called ATP • ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate
Adenine Ribose 2 Phosphate groups • ADP stands for adenosine diphosphate
All energy is stored in the bonds of compounds—breaking the bond releases the energy • When the cell has energy available it can store this energy by adding a phosphate group to ADP, producing ATP
ATP is converted into ADP by breaking the bond between the second and third phosphate groups and releasing energy for cellular processes.
Inside the Chloroplast • Thylakoids • Sack like photosynthetic membranes • Light reactions take place
Inside the Chloroplast • Grana • Stack of thylakoids
Inside the Chloroplast • Photosystems • Proteins in the thylakoid membrane which organize chlorophyll and other pigments into clusters. • Light collecting units of the chloroplast
Inside the Chloroplast • Stroma • Region outside of the thylakoid membranes • Where dark reactions ( Calvin Cycle) takes place
Chemistry Terms! • Reactant: a substance that changes during a chemical reaction. • Product: a substance produced during a chemical reaction. • Electron: a negatively charged part of an atom. It is the smallest of the 3 subatomic particles (neutron, proton, electron)
Electron Carriers • Transports high-energy electrons from the chlorophyll to other molecules on the Electron Transport Chain • NADP+ is an electron carrier…that accepts the electron and makes NADPH • NADPH is used to build various molecules such as glucose
Light Dependent Reaction • Occurs in the thylakoids • Needs light to occur, water, ADP and NADP+ • Produces ATP and NADPH • High-energy electrons move through the ETC and excite the pigments that are in the photosystems
Calvin Cycle • Named after Melvin Calvin (American Scientist) • Uses ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent reactions to produce high-energy sugars • Does not require light to occur • Dark reaction cycle • Light-independent cycle
Reactants • Diagram H2O CO2 Light NADP+ ADP + P Light Dependent Reaction Calvin Cycle ATP NADPH Chloroplast C6H12O6 Glucose O2 Products
Summary: • Light Dependent Reaction—H2O is broken down and light energy is stored temporarily in inorganic energy carriers, ATP and NADPH • Calvin Cycle—energy is transferred from ATP and NADPH to the organic compound glucose
Steps of Photosynthesis Light Reaction Process (occurs in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplast) • 1. Light gets absorbed through the thylakoid membranes • 2. Electrons get excited and move H+ down the Electron Transport Chain • 3. NADPH and ATP (Energy) are made • 4. Oxygen is Made and released Dark Reaction Process (Calvin Cycle) • Occurs in the Stroma • 5. NADPH and ATP are used to make glucose (C6H12O6)
Factors that Affect Photosynthesis • Shortage of Water • Plants in dry conditions (deserts) contain a waxy coating on their leaves. Which helps to keep moisture in. • Temperature • Temperature above or below the range of photosynthesis damage the enzymes which slows or stops the reaction from occurring • Intensity of light • Increasing the light intensity will increase the rate of photosynthesis
Exit Ticket-Final 5 • What are the products of the Light Reactions. (HINT: THERE ARE THREE THINGS) • Which of these products are used during the Dark Reactions. • What is another name for the Dark Reactions. • What are the products of the Dark Reactions. 5.:In your own words explain to me why plant stems are green and not red. (Make sure to have complete sentences, use scientific language, should be more than just ONE sentence!)