Maximizing Communications Impact Through Promotion Mix
480 likes | 510 Vues
Learn about promotion and marketing activities to influence consumers, integrated marketing communications, advantages & disadvantages of advertising, direct marketing, internet as an advertising medium, and importance of sales promotion in the marketing mix.

Maximizing Communications Impact Through Promotion Mix
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Promotions Dr. Mary Wolfinbarger Marketing 300
Promotion • Marketing activities used to communicate positive, persuasive info about an organization, its products and its activities to a target audience • Purpose: to directly or indirectly create sales, influence consumers.
To whom does promotion communicate? • Consumers/potential consumers • Interest groups/regulatory agencies • Current/potential investors • Society in general • Company employees
Integrated Marketing Communications • A planning concept recognizing the added value in integrating promo mix elements • Purpose: to provide clarity, consistency and maximum communications impact. • Explosion of communication choices made this more necessary • Technology made it more possible
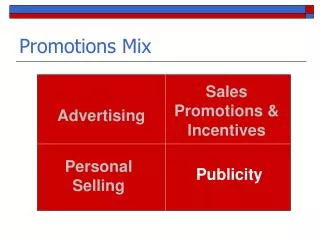
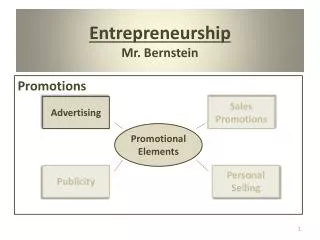
Promotion Mix • Advertising • Personal Selling • Sales Promotion • Public Relations
Advertising • A paid form of non-personal communication about an organization and/or its products to a target audience through a mass medium.
Media • TV • Newspapers • Radio • Magazines • Internet • Billboards • Etc….
Advantages • Can reach large mass audiences/ small niches • Usually cost efficient per person reached • Repetition of messages
Disadvantages • Absolute dollar outlay may be high • Response to ads (except retail ads) are slow • Advertising less persuasive than personal selling
Direct Marketing • Often included in advertising • Advantage: communicate directly with prospects • Can tailor messages for prospects • Messages can be longer/more complex • Can target best prospects
Direct Marketing • Biggest Disadvantage: Cost per person reached expensive (except for Internet email!)
Direct Marketing • Generate inquiries about prod. • Generate purchase • Gain trial • Increase usage • Enhance prod image w/ well-defined target audience
Direct Marketing • Gather information • Build ongoing relationships with customers
The Internet as An Advertising/ Direct Selling Medium • Point of sale ability (look and buy) • Potential for “mass customization” of ad messages • Advertising messages can be interactive and/or updated continuously
Advantages of Internet as Selling Medium • Primary form of online advertising (as of 2005): search (Google, Yahoo!, MSN) • Easy to measure effectiveness of search advertising • Banner Ads are now called Display Ads • The use of “rich media” in ads is increasing
Advantages of Internet as Selling Medium • Other forms: • sponsorship • ads in podcasts • ads embedded in online games (Massive Inc.) • viral games and videos • YouTube (sponsored and unsponsored) • Ad portals? veryfunnyads.com • Widgets • Mobile Advertising, Mobile search
Advantages of Internet as an Advertising Medium • Buyers often visit search engines and other web sites when in “purchase corridor” • Can change creative approach quickly • Click-through rates, page views, conversion rates easily tracked (“clickstream” data also)
Blogs/Social Networks/Discussion Groups • Robert Scoble’s book: Naked Conversations • Marketing junk is resisted (read “Flogs”) • Authenticity is expected • (well, with the exception of satirical blogs such as fakesteve.com) • Pretending to be someone you’re not may bring negative attention • Still, there is some “seeding” of discussions and some underground activity
Blogs/Social Networks/Discussion Groups • Internet buzz is not independent of other marketing mix variables • Advertising and other promotions increase buzz • Read “Five Rules of Underground Marketing” • http://www.clickz.com/showPage.html?page=3624847 • What are the 5 rules?
Personal Selling • Face to face communication with buyers to inform and persuade them to buy
Personal Selling • On average, companies spend more money/yr on personal selling than other elements of promo mix
Personal Selling Major Advantage: • More persuasive • Major Disadvantage • Costly per individual reached
Personal Selling Objectives: • Finding Prospects • Converting Prospects to Customers • Maintaining Customer Satisfaction
Personal Selling • Personal selling most likely for new, complex, and/or expensive products • The web now does some personal selling tasks • For example, Apple has a 20 minute sales presentation for the iPhone on its site • Cadillac has a site called mycadillacstory.com where celebrities and others post cadillac-related videos (soft sell, but it’s selling)
Sales Promotion • A direct inducement, offering added value or incentive for the product, to resellers, salespersons, or consumers.
Sales Promo • 25 yrs ago, % of spending on advertising was 70% • In recent years, about 25% • Shift largely been to trade promo • (But, the advertising pie has grown as well)
Sales Promo Why the shift? • Ad clutter • VCRs (zipping) • Channel surfing (zapping) • Various recessions
Sales Promo Why the shift? • Marketplace factors • similarity between goods • short term focus of managers • consumer expectations • private label competition
Common Objectives of Sales Promotion • Short term sales stimulation • Induce trial • Retain current customers/increase usage • Reinforce advertising efforts • Build trade support for campaign • Motivate sales force
Comments on Sales Promo “We’re in a very interesting phase in [sales] promotion. On one hand, we have had the meteoric advances of promotion understanding and consumer intelligence brought about by scanners and database management. Then on the other hand, we see the …. Success of Batman glasses at Taco Bell --
Comments on Sales Promo --over 4 million given away-- and we realize that it’s the same type of promotion America used to court movie goers on Saturday afternoons in the 1930s. It surely shows how human nature doesn’t change.” --William Robinson, Promotional Marketing
Two types: • Consumer-oriented (pull) • Trade-oriented (push)
Consumer Promotions • Samples • Coupons • Premiums • Contests and Sweepstakes • Price Discounts
Trade Promotions • Trade allowances • Dealer contest • POP • Co-operative advertising • Trade shows • Collateral materials • Price Discounts
Main Issue in Sales Promo • What is the long term impact on brand equity? (especially with price discounting)
Main Issue in Sales Promo Short term bribe point of view: • Buyers purchases on special deals often become less brand loyal
Main Issue in Sales Promo Long term sales building view: • Helps achieve shelf placement/ in-store display,thus increasing visibility • Consumers have little time to notice ad messages; sales promo get attention.
Main Issue in Sales Promotions Ideally: • Sales promo results in short term sales with long term equity building. • Both objectives needed in a competitive market.
More Comments on Sales Promotions “For years, sales promotion meant MDF funds (Market Development Funds, an innocuous word for slush money to pay off retailers for promoting your product), giant displays and tacky potholders. But now the industry has grown up…Marketers are looking to promotions to build their brand’s sales to insure a future for their brand’s tomorrow.” --William Robinson, Promotional Marketing
Publicity • Non-personal communication in news story form, regarding an organization and/or its products, transmitted through a mass medium at no charge. • The story is free; PR people are not
Public Relations • Brings advantage vs. advertising -- more credibility • Little control over message content or timing • PR takes great coordination/effort
Types of Publicity • News Release • Feature Article • Press Conference • Letters to the Editor • Editorial • Special Events
Integrated Marketing Communications and PR • Complements event sponsorship & trade shows • New products with special angles can be supported by PR • Marketing campaigns with a special “hook” are newsworthy
PR Objectives • Informing buyers how to select, buy or use your product • Dispelling negative info about brand • Build store traffic • Support event sponsorships, trade shows, other promo activities • Persuade target audience to purchase brand
Informative Promotion • Increase awareness • Explain how product works • Suggest new uses • Build company image Goals and Tasks of Promotion
Persuasive Promotion Goals and Tasks of Promotion • Encourage brand switching • Change customers’ perceptions of product attributes • Influence immediate buying decision • Persuade customers to call
Reminder Promotion Goals and Tasks of Promotion • Remind customers that product may be needed • Remind customers where to buy product • Maintain customer awareness
Action Desire Conative (doing) Interest Affective (feeling) Attention Cognitive (thinking) The AIDA Concept Different promotional methods are better at different parts of AIDA – also we can evaluate an entire marketing communication effort by evaluating the success we are having with consumers at each step of the model.