After studying this unit
450 likes | 619 Vues
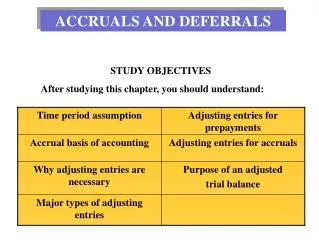
After studying this unit. You will be able to: Recognize a variety of professional kitchen tools and equipment Select and care for knives Understand how a professional kitchen is organized. Importance of Proper Tools and Equipment.

After studying this unit
E N D
Presentation Transcript
After studying this unit • You will be able to: • Recognize a variety of professional kitchen tools and equipment • Select and care for knives • Understand how a professional kitchen is organized
Importance of Proper Tools and Equipment Having the proper tools and equipment for a particular task may mean the difference between a job well done and one done carelessly, incorrectly or even dangerously.
NSF International • Promulgates consensus standards for the design, construction and installation of kitchen tools, cookware and equipment
Standards for Tools and Equipment • Must be easy to clean • All food contact surfaces must be nontoxic (under intended end-use conditions), nonabsorbent, corrosion resistant and nonreactive • All food contact surfaces must be smooth, free of pits, cracks, crevices, ledges, rivet heads and bolts
Standards for Tools and Equipment (cont.) • Internal corners and edges must be rounded and smooth; external corners and angles must be smooth and sealed • Coating materials must be nontoxic and easily cleaned; coating must resist chipping and cracking • Waste and waste liquids must be easily removed
Selecting Tools and Equipment Before purchasing or leasing any equipment, you should evaluate several factors: • Is this equipment necessary for producing menu items? • Will this equipment perform the job required in the space available? • Is this equipment the most economical for the operation’s specific needs? • Is the equipment easy to clean, maintain and repair?
Hand Tools • Hand tools are designed to aid in cutting, shaping, moving or combining foods; they have few, if any moving parts
Knives • The most important item in the tool kit • A good knife begins with a single piece of metal, stamped, cut, or best of all, forged and tempered
The Blades • Carbon steel • Stainless steel • High carbon stainless steel • Ceramic
The Shapes • French or chef’s knife • Boning knife • Paring knife • Cleaver • Slicer • Butcher knife or scimitar • Oyster and clam knives • Japanese knives
Japanese Knives Yanagiba Sashimi Knife Usuba Knife Deba Knife
Measuring and Portioning Devices • Scales • Are necessary to determine the weight of an ingredient or portion of food • Volume measures • Ladles • Portioning scoops • Measuring cups • Measuring spoons
Thermometers • Stem-type thermometers, including instant-read models, are inserted into food to obtain temperature readings
Calibrating Stem-Type Thermometers • Fill a glass with shaved ice • Place thermometer in ice slush • Adjust to 32ºF following the manufacturer’s directions • Check calibration • Repeat, substituting boiling water • Calibrate thermometer to 212ºF
Cookware • Cookware includes range top pots and pans as well as the pans that are used in the oven
Metal and Heat Conduction • Copper • Aluminum • Stainless Steel • Cast Iron
Other Materials Used in Cookware • Glass • Ceramic • Plastic • Enamelware • Nonstick • Silicone bakeware
Common Cookware Common Saucepan Rondeau / Brazier Sauteuse (Sloped Sides) Sautoir (Straight Sides)
Common Cookware (cont.) Hotel Pans Stock Pot with Spigot Wok
Processing Equipment • Slicer • Mandoline • Food chopper or buffalo chopper • Food processor • Blender • Immersion blender • Mixer • Juicer
Heavy Equipment • Heavy equipment includes the gas, electric or steam operated appliances used for cooking, reheating or holding food; these items are usually installed in a fixed location
Stove Tops Flat-Top Range Gas burner and griddle with dual ovens and an overhead broiler
Specialized Equipment for New Culinary Techniques Immersion Heat Circulator and Thermal Bath
Buffet Equipment • Specialized equipment is used to ensure that food is handled safely and efficiently and displayed properly
Safety Equipment (cont.) • Ventilation systems • Ventilation hoods • First-aid kits • Protective gear
The Professional Kitchen • The kitchen is the heart of the food service operation • Work is broken into work sections and work stations • When designing a kitchen, it is important to use the space wisely so that each of its functions can be accomplished efficiently