Cubic Curve Sketching
70 likes | 299 Vues
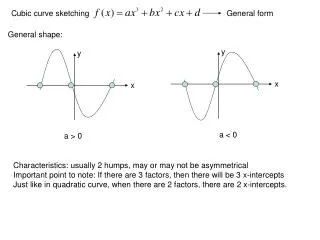
Cubic Curve Sketching. Basic cubic shapes . Unlike quadratics cubic usually have two bumps e.g. But sometimes the have no bumps. y =x 3 -3x 2 +3. y =-x 3 +3x 2 +3. y =x 3. Example: Sketch y=(x-1)(x+2)(x+3). Here are the steps for sketching cubic curves

Cubic Curve Sketching
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Basic cubic shapes Unlike quadratics cubic usually have two bumps e.g. But sometimes the have no bumps y=x3 -3x2 +3 y=-x3 +3x2 +3 y=x3
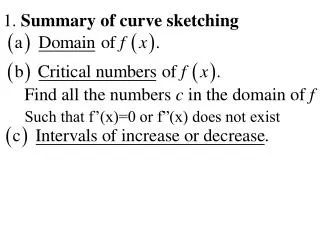
Example: Sketch y=(x-1)(x+2)(x+3) Here are the steps for sketching cubic curves Find x intercepts by solving y=0 Find y intercept by putting x=0 Find out what happens as x get very big and very small (Limits)
Find x intercepts by solving y=0 Solve: (x-1)(x+2)(x+3)=0 Equate factors to zero X-1=0 X+2=0 X+3=0 Intercepts are: x=1, x=-2, x=-3
2. Find y intercept by putting x=0 y=(0-1)(0+2)(0+3) y= -6
3. Find out what happens as x get very big and very small (Limits) If x3 has a positive coefficient (multiplier) then as x -> ∞ y -> ∞ If x3has a negative coefficient then as x -> ∞ y -> - ∞ In our example y=(x-1)(x+2)(x+3) The coefficient of x3 is 1 so as x -> ∞ x -> ∞
Here is the final sketch y=(x-1)(x+2)(x+3)