The Rise and Impact of City-States in Ancient Mesopotamia
80 likes | 200 Vues
Explore the fascinating evolution of Mesopotamian city-states, which emerged in the “Fertile Crescent” between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. Learn how environmental factors shaped these early civilizations' culture and technology. Discover the significance of city-states like Ur and Uruk, their unique governance systems, and their roles as economic and spiritual centers. Uncover the innovations they pioneered, from agriculture to trade, and how these developments influenced relationships in the modern Middle East, warfare, and the social hierarchy, including the role of slavery.

The Rise and Impact of City-States in Ancient Mesopotamia
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Mesopotamia From City-States to Gilgamesh
Essential Questions • How did environment affect the early Mesopotamian civilizations, including culture and technology? • How did the Mesopotamian system of city-states affect technology, culture, and modern Middle East relations ? • How do city-states relate to Civilization?
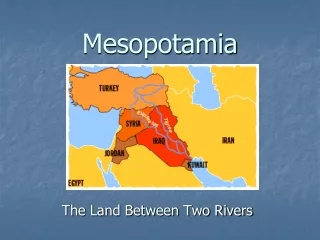
Mesopotamia • Land between the rivers (Tigris and Euphrates) • “Fertile Crescent” • Modern day Iraq • Sumer – *1stCivilization
The Rise of City-States • City-state = a city with political and economic control over the surrounding area • Huh? • In English = small like a city but has own government, military, economy, and identity (not part of a state or country) • Eridu, Ur, Uruk
Building of city-states • Walled cities (made of mud brick) • Why mud brick? • Close to water • Euphrates flooded • Explanation • Angry gods • How do you appease them?
Ziggurats • Physical, economic, political, and spiritual center of city-state • Top of ziggurat was a temple • Gods and Goddesses in complete control • Allowed mortals power (kingship was divine (theocracy = gov’t by divine authority) • Uruk dedicated to Ishtar
Accomodated Farming • Economy based chiefly on farming until… • Trade and industry develop…leads to • Development of technology such as… • Wheel (Wheeled carts for easier transportation) and… • Advanced weapons which leads to… • Warfare and competition
Slavery • Very common in ancient world (agriculture-based societies) • NOT racially based • In Sumer slaves 1 of 3 social classes • Nobles (kings, priests, priestesses) • Commoners