An Algorithm for Checking Normality of Boolean Functions
220 likes | 372 Vues
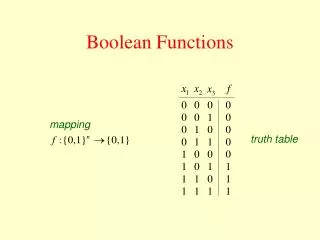
This paper introduces a novel algorithm for checking the normality of Boolean functions, which identifies whether a given Boolean function is affine or constant across various dimensions. The motivation stems from the open question regarding the existence of non-normal bent functions. By enumerating m-dimensional flats, the algorithm improves upon naive approaches, significantly reducing complexity. The method facilitates the determination of flat properties, enabling faster checks for normality and related applications like the Maiorana-McFarland property.

An Algorithm for Checking Normality of Boolean Functions
E N D
Presentation Transcript
An Algorithm for Checking Normality of Boolean Functions Magnus Daum Hans Dobbertin Gregor Leander
Overview • Definitions and Motivation • General Idea and Algorithm • Details of the Algorithm • Complexity Evaluations Daum,Dobbertin,Leander: An Algorithm for Checking Normality of Boolean Functions
Definitions • Boolean function , n=2m • f is normal :,9 m-dimensional flat a+U: is constant • f is weakly normal :,9 m-dimensional flat a+U: is affine Daum,Dobbertin,Leander: An Algorithm for Checking Normality of Boolean Functions
Motivation • Open question: Are there non normal bent functions? • Dillon / Dobbertin found some new bent functions to be checked for normality (Kasami power functions) • Interesting cases: m ¸ 5 odd (i.e. n=10,14,…) Daum,Dobbertin,Leander: An Algorithm for Checking Normality of Boolean Functions
# (flats of of dimension m) Motivation: Naive Algorithm • Naive idea: • Enumerate all flats of dimension m and check whether f is constant/affine or not • # ( flats of of dimension k): • # (subspaces of of dimension k): Daum,Dobbertin,Leander: An Algorithm for Checking Normality of Boolean Functions
constant General Idea • flat a+U, u1,…,uk a basis of U • f is affine on a+U: ) f is constant on a+U or • f constant on a+U: Daum,Dobbertin,Leander: An Algorithm for Checking Normality of Boolean Functions
) and are constant General Idea Daum,Dobbertin,Leander: An Algorithm for Checking Normality of Boolean Functions
General Idea • Idea for the algorithm: • find flats a+U and b+U, dim(U)=k • combine them to with : Daum,Dobbertin,Leander: An Algorithm for Checking Normality of Boolean Functions
a+U, b+U, dim U=k ! dim=k+1 a+U, b+U, dim U=k ! dim=k+1 repeat up to dim=m-1 combine Outline of the Algorithm Input: Boolean function f, starting dimension t0 For all subspaces do : Determine all flats a+U, such that m-dimensional flats on which f is affine Daum,Dobbertin,Leander: An Algorithm for Checking Normality of Boolean Functions
Outline of the Algorithm • Main problem: can be split into in many ways • many ways to find some • try to avoid this redundant work Daum,Dobbertin,Leander: An Algorithm for Checking Normality of Boolean Functions
(ui): index of the leftmost 1 in ui Details: Representation of U Details • need a unique representation of U to avoid looking at same U twice • Basis of U is a Gauss Jordan Basis • >: standard lexicographical ordering Daum,Dobbertin,Leander: An Algorithm for Checking Normality of Boolean Functions
Details: Representation of U • Example: • easy to enumerate all subspaces: • loop over all • fill corresponding to this scheme • loop over all values in for Daum,Dobbertin,Leander: An Algorithm for Checking Normality of Boolean Functions
Details: Representation of U • Example: • easy to enumerate all flats corresponding to U: • a+U can be represented uniquely as a‘+U with a‘2 Daum,Dobbertin,Leander: An Algorithm for Checking Normality of Boolean Functions
if is GJB otherwise Details: Combining Flats • Main data structure: List of all flats corresponding toon which f is constant equal to c Daum,Dobbertin,Leander: An Algorithm for Checking Normality of Boolean Functions
compute once , check Details: Combining Flats • store elements in sorted order Lemma: Daum,Dobbertin,Leander: An Algorithm for Checking Normality of Boolean Functions
only need to consider if this is fulfilled or Details: Combining Flats Corollary: Daum,Dobbertin,Leander: An Algorithm for Checking Normality of Boolean Functions
Details: Algorithm Input: Boolean function f, starting dimension t0 Output: a list of all flats on which f is affine Daum,Dobbertin,Leander: An Algorithm for Checking Normality of Boolean Functions
Complexity • How to choose starting dimension t0? • evaluate expected complexity under the assumption that f is a random Boolean function • Two parts: • „exhaustive search“ part • „combining“ part Daum,Dobbertin,Leander: An Algorithm for Checking Normality of Boolean Functions
Complexity: Exhaustive Search • Check all flats of dimension t0: about flats • less than two comparisons per flat on average n=14: Daum,Dobbertin,Leander: An Algorithm for Checking Normality of Boolean Functions
Complexity: Combining • complexity of combining part • n=14: • exh.search: • choose starting dimension t0=2 or t0=3 • implementation on Pentium IV, 1.5 GHz: about 50 hours for n=14 naive algorithm Daum,Dobbertin,Leander: An Algorithm for Checking Normality of Boolean Functions
Conclusion • presented an algorithm that computes a list of all flats, on which a given Boolean function is affine/constant • can be used to check (weak) normality of Boolean functions much faster than with the naive algorithm • other applications also possible(like checking Maiorana-McFarland-property) • solved open question about existence of non (weakly) normal bent functions Daum,Dobbertin,Leander: An Algorithm for Checking Normality of Boolean Functions