Harmonic Motion ( IV )
100 likes | 121 Vues
Learn about the energy dynamics of a simple harmonic oscillator in this insightful physics lecture. Discover the total energy equation and its components - kinetic and potential energy. Explore scenarios involving changing amplitudes, velocities, and accelerations in harmonic motion. Dive into examples to calculate total energy, amplitudes, velocities, and accelerations of block-spring systems. Gain a deeper understanding of energy transformations in simple harmonic motion through practical illustrations.

Harmonic Motion ( IV )
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Harmonic Motion (IV) • Energy of a simple harmonic oscillator Physics 1D03 - Lecture 34
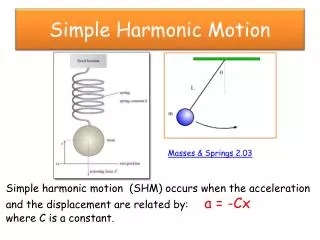
Energy of a SHO Recall: ETot = K + U = 1/2mv2 + 1/2kx2 for a spring. But we know that: x=A cos(ωt+φ) v=-A ω sin(ωt+φ) Physics 1D03 - Lecture 34
M Energy in SHM Look again at the block & spring Hence: ETot = ½kA2 We could also write E = K+U = ½ m(vmax )2 Physics 1D03 - Lecture 34
Concept Quiz Suppose you double the amplitude of the motion, what happens to the maximum speed ? • Doubles • 4 x Larger • Doesn’t change Physics 1D03 - Lecture 34
Concept Quiz • Suppose you double the amplitude of the motion, what • happens to the maximum acceleration? • Doubles • 4 x Larger • Doesn’t change Physics 1D03 - Lecture 34
Concept Quiz • Suppose you double the amplitude of the motion, what • happens to the the total energy? • Doubles • 4 x Larger • Doesn’t change Physics 1D03 - Lecture 34
Energy Since we know the total energy of a SHM, we can calculate the or displacement velocity at any point in time: ETot=1/2kA2 = K+U = 1/2mv2 + 1/2kx2 So, if x=0, all E is in kinetic, and v is at max if x=A, all E is in potential, and v is zero Physics 1D03 - Lecture 34
Example A 100g block is 5cm from the equilibrium position moving at 1.5m/s. a) What is the total energy of the system ? b) What is the amplitude of the oscillations ? Physics 1D03 - Lecture 34
Example A 500g block on a spring is pulled 20cm and released. The motion has a period of 0.8s. What is the velocity when the block is 15.4cm from the equilibrium ? Physics 1D03 - Lecture 34
Example A 1.0kg block is attached to a spring with k=16N/m. While the block is at rest, a student hits it with a hammer and almost instantaneously gives it a speed of 40cm/s. • what is the amplitude of the subsequent oscillations ? • what is the block’s speed at the point where x=A/2 ? Physics 1D03 - Lecture 34