Understanding Isotopes: Characteristics, Examples, and Dalton's Atomic Theory
110 likes | 258 Vues
This overview explores isotopes, focusing on potassium (K) isotopes and their defining characteristics. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with identical proton numbers but differing numbers of neutrons. We highlight examples, such as Potassium-39 and its variations, alongside Dalton's Atomic Theory. This theory posits that all matter consists of atoms, which are uniform within an element but distinct across different elements. The differences in isotopes lead to variations in mass and physical properties while maintaining similar chemical behavior due to identical electron configurations.

Understanding Isotopes: Characteristics, Examples, and Dalton's Atomic Theory
E N D
Presentation Transcript
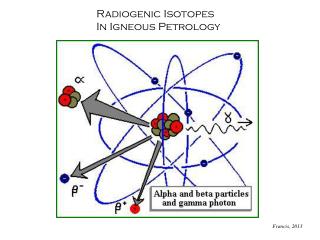
There are 3 isotopes of K atoms 19 19 19 19 19 19 21 22 20
What are isotopes? • ATOMS OF THE SAME ELEMENT: • WITH the same # of • but DIFFERENTNUMBER OF p+ NEUTRONS
5 Postulates of Dalton’s Atomic TheoryWhich two are incorrect?.......Why? All matter is made of extremely small particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass, and chemical properties. Atoms of a specific element are different from those of any other element. Atoms cannot be created, divided into smaller particles, or destroyed. Different atoms combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. In a chemical reaction, atoms are separated, combined, or rearranged.
Two ways to write the symbol for an isotope: 1. 2. Mass # 39 K Potassium- 39 19 Atomic # Mass Number = # protons + # neutrons
How many p+, e-, & n0 are contained in each of the following atoms? 1. gallium - 64 p+ = 31 e- = 31 64-31 n0= 33 p+ = 55 e- = 55 • 132 Cs 55 132-55 n0= 77
Isotope Similarities: a. Same # of p+ and e- b. Chemically and Physically alike Why? Same # of valence electrons determine chemical behavior
Isotope Differences: a. Different # of neutrons b. Different mass numbers c. Different masses
22 Ne 10 10 10 12 10 46 Ca 20 46 20 20 20