Bones
240 likes | 750 Vues
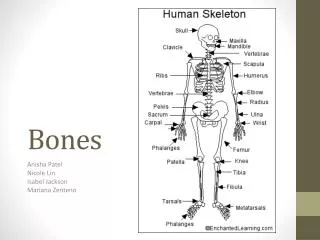
Bones. Anisha Patel Nicole Lin Isabel Jackson Mariana Zenteno. Bone Classification. Long Bones: forearm and thigh bone Short Bones: Bones in the wrists and ankles Flat Bones: Ribs and part of the skull Irregular Bones: Bones within the vertebrae Round Bones: Knee cap.

Bones
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Bones Anisha Patel Nicole Lin Isabel Jackson Mariana Zenteno
Bone Classification • Long Bones: forearm and thigh bone • Short Bones: Bones in the wrists and ankles • Flat Bones: Ribs and part of the skull • Irregular Bones: Bones within the vertebrae • Round Bones: Knee cap
Microscopic Structure • Compact bones • No gaps, osteon units make up the Haversian systems • Spongy Bones: No central canals • Osteocytes: Bone cells
Vocabulary • Haversian system, or osteon – the structural unit of compact bone • Lamella – weight-bearing, column-like matrix tubes composed mainly of collagen • Haversian, or central canal – central channel containing blood vessels and nerves • Volkmann’s canals – channels lying at right angles to the central canal, connecting blood and nerve supply of the periosteum to that of the Haversian canal • Osteocytes – mature bone cells • Lacunae – small cavities in bone that contain osteocytes • Canaliculi – hairlike canals that connect lacunae to each other and the central canal
Cells within the Bones • Osteoblasts – bone-forming cells • Osteocytes – mature bone cells • Osteoclasts – large cells that resorb or break down bone matrix • Osteoid – unmineralized bone matrix composed of proteoglycans, glycoproteins, and collagen
Bone Development • Osteogenesis and ossification – the process of bone tissue formation, which leads to: • The formation of the bony skeleton in embryos • Bone growth until early adulthood • Bone thickness, remodeling, and repair
Classification of Breaks • Bone fractures are classified by: • The position of the bone ends after fracture • The completeness of the break • The orientation of the bone to the long axis • Whether or not the bone ends penetrate the skin
Types of Fractures • Greenstick – incomplete and the break occurs on the convex surface of the bend in the bone • Fissured – an incomplete longitudinal break • Comminuted – fracture is complete and fragments the bone • Transverse – complete, and the break occurs at a right angle to the axis of the bone • Oblique – at an angle other than a right angle to the axis of the bone • Spiral – caused by twisting a bone excessively
Stages of a Healing Bone • Hematoma • Fibrocartilage callus forms • Granulation tissue (soft callus) forms a few days after the fracture • Capillaries grow into the tissue and phagocytic cells begin cleaning debris • Bony callus formation • Bone remodeling
JOINTS • Fibrous Joints • dense connective tissues connect bones • between bones in close contact • Cartilaginous Joints • hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage connect bones • Synovial Joints • most complex • allow free movement • synarthrotic • immovable • amphiarthrotic • slightly movable • diarthrotic • freely movable
Fibrous Joints • 3 Types • Syndesmosis • Fibrous sheet that connects the bones together • amphiarthrotic • Suture • Thin layer of connective tissue that connects two bones together • Synarthrotic • Gomphosis • Cone shaped • Synarthrotic
Cartilaginous Joints • 2 Types • Synchondrosis • Hayline cartilage • Synarthrotic • Symphysis • Pad of fibrocartilage that lies between two bones • Amphiarthrotic
Synovial Joints • Diarthrotic • Contains Synovial Fluid
Types of Synovial Joints • Ball-and-Socket joint • Hip or shoulder • Condyloid Joint • Joints in the Metacarpals and Phalanges
Gliding Joint • Between Carpals and tarsals • Hinge Joint • Elbow
Pivot Joint • Between the radius and Ulna • Saddle Joint • Between carpals and metacarpals
Joint Disorders • Sprains • damage to cartilage, ligaments, or tendons associated with joints • forceful twisting of joint • Bursitis • inflammation of a bursa • overuse of a joint • Arthritis • inflamed, swollen, painful joints • Rheumatoid Arthritis • Osteoarthritis • Gout