Introduction to Logarithms
140 likes | 260 Vues
This lesson provides a comprehensive overview of logarithms, focusing on exponential growth and decay. It introduces key concepts such as initial value (y-intercept) and growth/decay rates. We explore a practical example involving a bacteria population that doubles every hour, starting from an initial sample of 40. The lesson poses questions about calculating population after a certain duration and determining the time needed to reach a specific population. Additionally, we cover finding the inverse of exponential functions and their application in real-world scenarios.

Introduction to Logarithms
E N D
Presentation Transcript
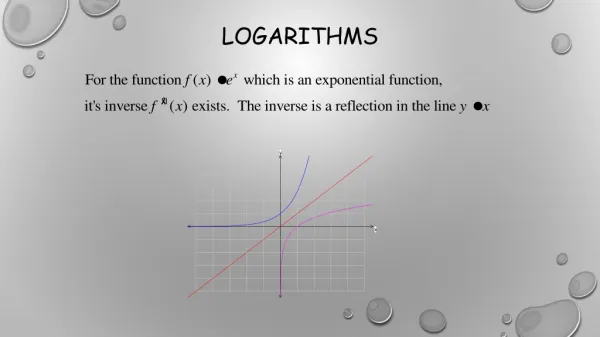
Introduction to Logarithms Lesson 7.3
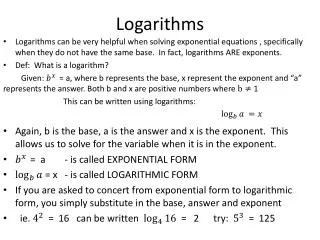
Review: y = abx • a: initial value/y-intercept • b: growth rate • Growth: b > 1 • Decay: 0 < b < 1
A bacteria population doubles every hour. If you start with a sample of 40 bacteria, how many will there be in 3 hours?
A bacteria population doubles every hour. If you start with a sample of 40 bacteria, after how many hours will there be 1000 bacteria present?
a power m n b
2 0 4 4 2 0
-3 -1 -2 -2 -1 -3
2 .903 .602 1.857
2.079 1 1.099 1 0 -.288