Angiosperms
180 likes | 659 Vues
Angiosperms. Noor Hamideh Shereen Abbas. Introduction. Angiosperms are plants that produce flowers and form seeds within an ovary that develops into a fruit. Latin for ‘closed seed’ Most common land plants (~250,000 species) Reproduce sexually by pollination. Angiosperm Diversity.

Angiosperms
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Angiosperms Noor Hamideh ShereenAbbas
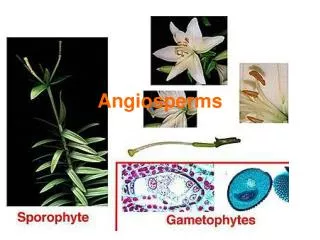
Introduction • Angiosperms are plants that produce flowers and form seeds within an ovary that develops into a fruit. • Latin for ‘closed seed’ • Most common land plants (~250,000 species) • Reproduce sexually by pollination
The Flower • Reproductive structure • Sepals and Petals: Outer part of flower • Stamen: Male reproductive part • Anther: Produces pollen grains containing sperms • Carpel: Female reproductive part • Ovary: Produces eggs inside ovule, develops into fruit • Ovule: Houses egg, develops into seed • Stigma: The carpal opening
Life Cycle • Requires a good, moist environment • Seeds and ovules are well protecteddue to the flower structure • The ovum must be fertilized by a sperm cell contained in a pollen grain • The fertilized egg develops into an embryo contained in a seed contained in a fruit • The fruit cannot develop unless the seed is fertilized
1. Pollination • Pollination is the transfer of pollen from the anther of a stamen to the stigma of a carpal. • Self pollination: Pollen from the same plant fertilizes the egg cell of that plant • Cross pollination: More common, pollen is transferred from one plant to another (of the same species) by wind, water, or animals. • Flowers are adapted to one of these methods
2. Fertilization • Pollen grain lands on stigma • Pollen tube grows down into ovary • 1 of 2 nuclei in the pollen divides into 2 sperm nuclei • 1 nucleus fuses with the egg to produce a fertilized egg • The other nucleus fuses with the ovule to become endosperm tissue, that provides nutrition • The ovule becomes a seed, and the ovary a fruit. • Other flower parts die
3. Seed Dispersal • Seed dispersal is the way seeds find soil in which to germinate(sprout), it includes: • Being blown by wind (ex: dandelion) • Being carried on water • Having hooks that attach to fur • Being eaten by animals and excreted into soil
TheEnd Noor Hamideh ShereenAbbas